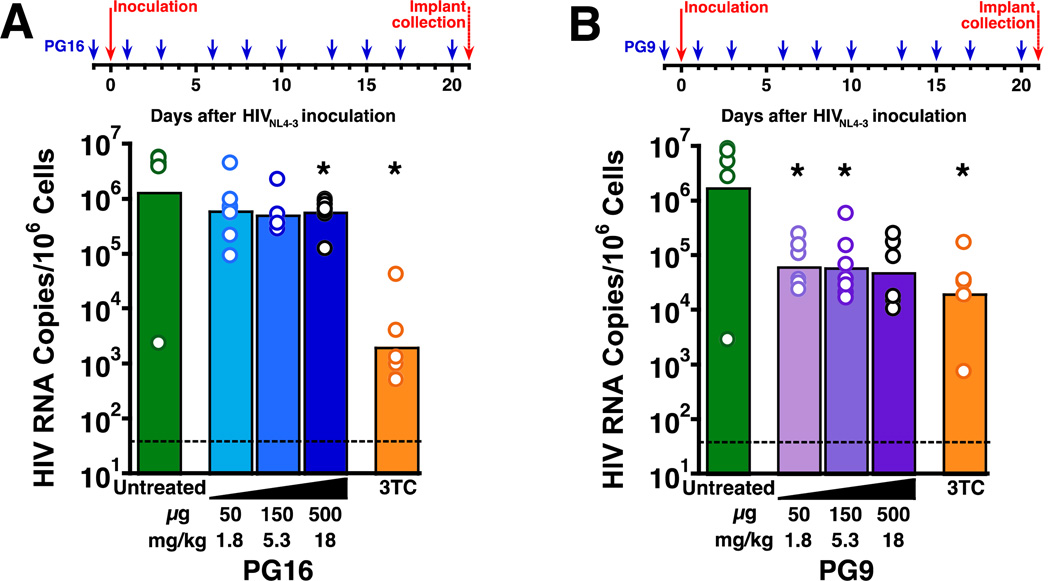
Fig. 4. PG16 and PG9 exhibited minimal protective activity in SCID-hu Thy/Liv mice challenged with HIVNL4-3.
(A) Statistically significant reductions in HIV RNA occurred in mice treated i.p. with 500 µg PG16 three times per week beginning the day before inoculation and continuing until implant collection at 21 days. Much larger (~3 log10) reductions in HIV RNA were observed in mice treated i.p. with 30 mg/kg 3TC once daily beginning the day before inoculation until implant collection. (B) Statistically significant reductions of >1 log10 in HIV RNA occurred in mice treated i.p. with 50 and 150 µg PG9 three times per week beginning the day before inoculation and continuing until implant collection at 21 days (P=0.055 for 500 µg PG9). Comparable reductions in HIV RNA were observed in mice treated i.p. with 30 mg/kg/day 3TC once daily beginning the day before inoculation until implant collection. The columns represent means, and the open circles represent individual mice. *P<0.05 compared to untreated HIV-infected mice by the Mann-Whitney U test. The dotted line indicates the HIV RNA detection limit. (101.5 copies per 106 implant cells).