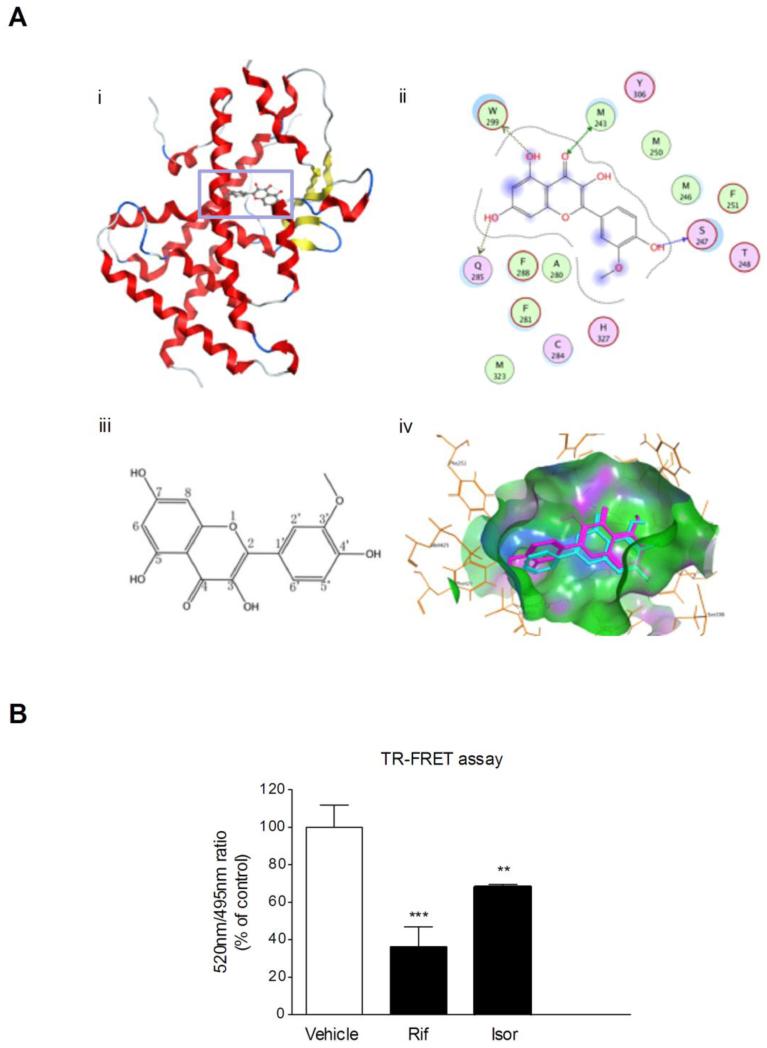
Figure 6.
Molecular docking analyses and TR-FRET assay. (A) Molecular docking of isorhamnetin to hPXR ligand-binding domain. i) Docking mode of isorhamnetin in the binding site of hPXR (shown in ribbon representation and colored by Terminus). ii) 2D-interaction schematic diagram of isorhamnetin docking to the hPXR ligand-binding domain was generated by the Ligand Interactions module of MOE. The binding-site residues are colored according to different types, with hydrophobic residues in green, polar residues in purple and charged residues highlighted with bold contours. Blue spheres and contours indicate matching regions between ligand and receptor. Hydrogen-bond interactions are shown by green dotted lines with arrows for side chain and main chain interactions, respectively. iii) Molecular structure of isorhamnetin. iv) The binding poses of isorhamnetin (purple) in the ligand-binding pocket of hPXR. (B) The interaction between isorhamnetin and the ligand-binding pocket of hPXR was further characterized using a LanthaScreen TR-FRET PXR competitive binding assay system. The TR-FRET ratio was calculated by dividing the emission signal at 520nm by that at 495nm. Data are expressed at means ± SD of quadruplicate of a representative experiment. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001 vs. vehicle-treated wells.