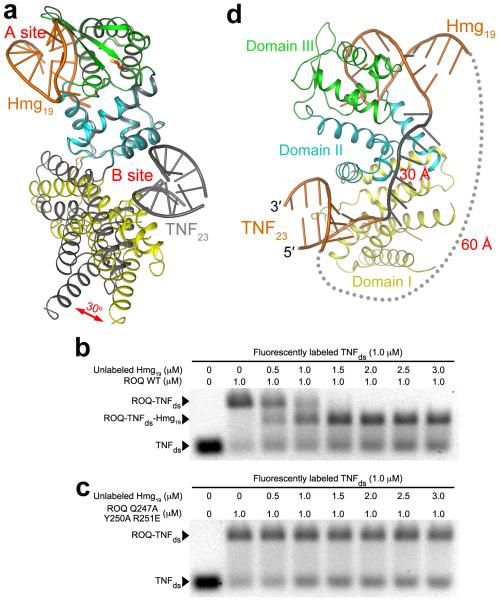
Figure 5. Two separate RNA binding sites in the ROQ domain.
(a). Overlay of the structures of the Hmg19 complex (in color) and TNF23 complex (gray) of the ROQ domain, based on domains II and III. A 30° change in the orientation of domain I is indicated with the red arrow. (b). EMSA results showing the formation of the ROQ-TNFds-Hmg19 ternary complex. Wild-type ROQ domain was pre-incubated with labeled TNFds, and then with increasing concentrations of unlabeled Hmg19. The NaCl concentration was 50 mM. (c). EMSA results with mutations in the A site. The mutations blocked the formation of the ternary complex. (d). A model showing possible linkages between the RNA molecules in the B site and A site. A single-stranded RNA (gray, 7 nts) was modeled to connect the 3′ end of the RNA in the B site to the 5′ end of the stem-loop RNA in the A site (~30 Å distance). A linker between the 3′ end of the RNA in the A site to the 5′ end of the RNA in the B site would need to span ~60 Å (gray dots).