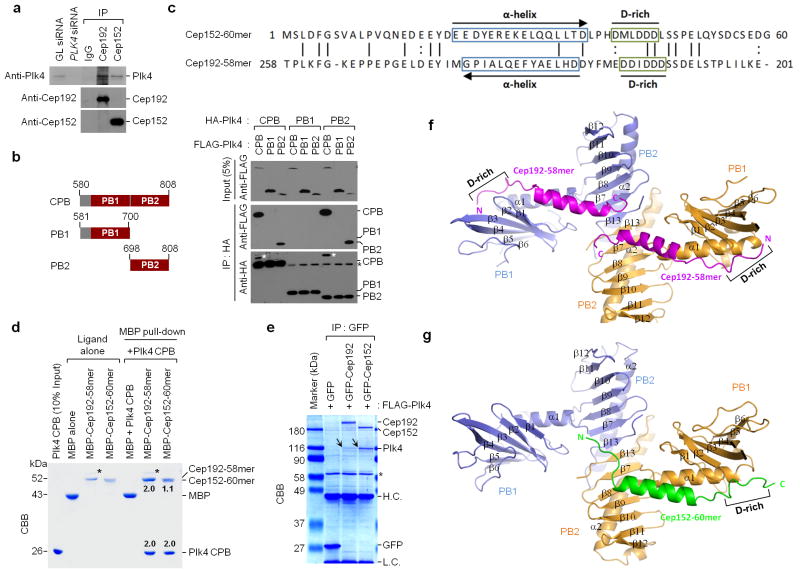
Figure 2.
Biochemical and structural analysis of Plk4 CPB in complex with Cep192-58mer or Cep152-60mer. (a) Interaction of Plk4 with Cep192 and Cep152 at endogenous levels. HeLa cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis with the indicated antibodies cross-linked to agarose beads. GL siRNA, Luciferase siRNA; IgG, control rabbit IgG. (b) Immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis was performed with 293T cells cotransfected with the indicated constructs. White asterisks, remaining FLAG-Plk4 CPB signals from the second panel immunoblot; Black asterisks, non-specific bands from IgG light chain. (c) Reverse alignment of Cep152-60mer and Cep192-58mer. Identical (vertical line) and conserved (colon) residues are indicated. (d) MBP pull-downs were performed using purified proteins. CBB, Coomassie-stained gel; asterisks, contaminated proteins; numbers, the relative amount of Cep192-58mer or Cep152-60mer bound to a CPB dimer (2.0). (e) Immunoprecipitation (IP) analysis with 293T cells cotransfected with the indicated constructs. To achieve stable overexpression, a kinase-inactive Plk4 K41M mutant was used. CBB, Coomassie-stained gel; arrows, coimmunoprecipitated FLAG-Plk4; asterisk, cross-reacting protein; H.C. and L.C., IgG heavy and light chains. (f,g) Overall structures of the CPB–Cep192-58mer and the CPB–Cep152-60mer complexes. Each subunit (blue or orange) of a homodimeric CPB consists of PB1 and PB2 folds. N, N-terminus; C, C-terminus; D-rich, D-rich motif. Uncropped blot images for a and b are shown in Supplementary Figure 8b,c.