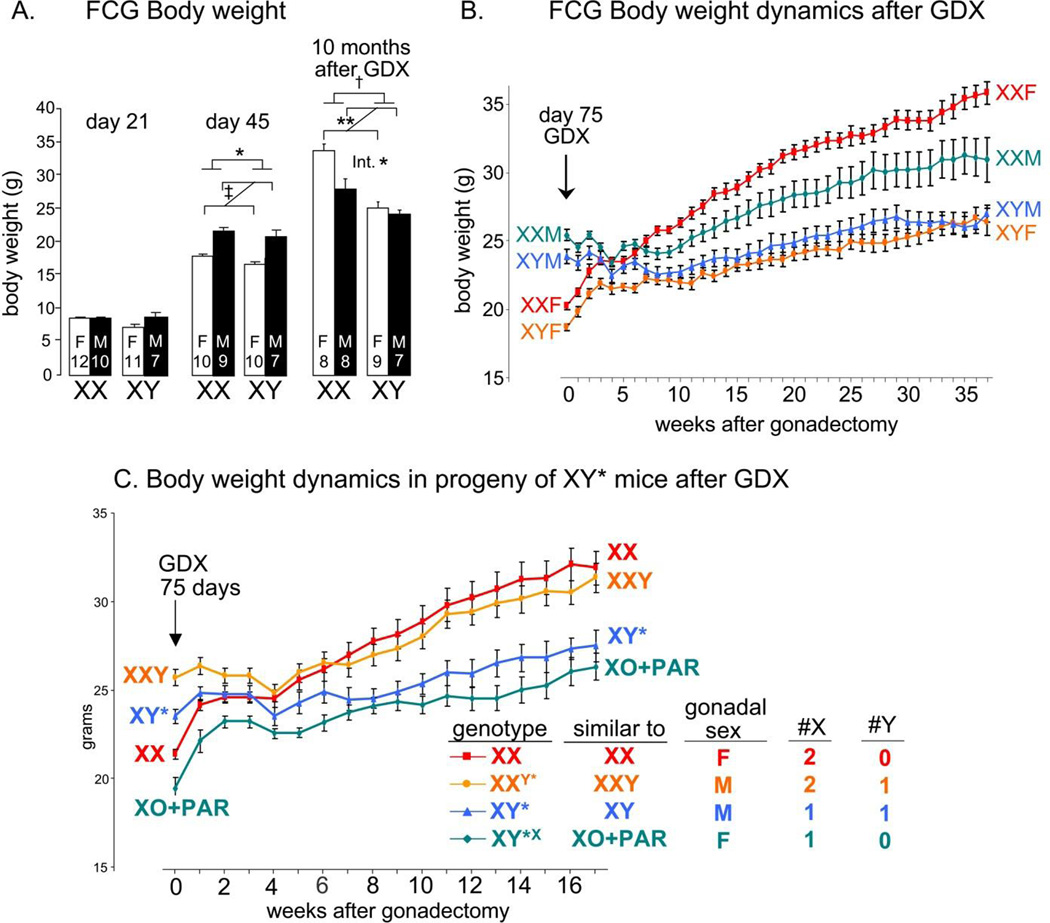
Figure 3.
Using Four Core Genotypes (FCG) and XY* models to dissect sex-biasing factors causing sex differences in body weight. The FCG model varies sex chromosome complement and gonadal type independently, producing four groups: XXM, XX gonadal males; XYM, XY gonadal males; XXF, XX gonadal females; XYF, XY gonadal females. See text and Figure 2 for further discussion of this model. A. FCG mice showed no group differences in body weight at day 21 after birth. By day 45, secretion of gonadal hormones makes gonadal males heavier than gonadal females (‡ p<0.000001), but XX mice weigh slightly more than XY (*p<0.05). Ten months after gonadectomy (GDX at 75 days of age), XX mice are 24% heavier than XY mice († p<0.0001). The effects of sex chromosome complement and gonadal sex interacted significantly (Int, *p<0.05) because XX gonadal females are heavier than gonadal males, but XY gonadal males and females are not different. ** p<0.01 B. Body weight in gonadally intact FCG mice at day 75 and after GDX at day 75. In gonadally intact mice (week 0), when all sex-biasing factors are operating, gonadal males are 25–28% heavier than gonadal females, but XX mice are 6–9% heavier than XY mice. The sex difference caused by activational effects of gonadal secretions disappears in the first month after GDX, after which XX mice gain more weight than XY mice until the sex chromosome effect is nearly as large at 10 months after GDX as the activational effect was prior to GDX. The difference between mice with XX and XY sex chromosome complement is reduced when gonads are present. C. The XY* model varies the number and type of sex chromosomes as shown here and in Figure 2, with two gonadally female groups and two gonadally male groups. Gonadally intact progeny of XY* at 75 days of age (week 0) show greater body weight in the gonadally male groups. After GDX at 75 days of age, the activational effects of gonadal hormones are lost (little difference between gonadal males and females) but mice with two X chromosomes gain weight more than mice with one X chromosome (p<0.000001). The presence of the Y chromosome has little effect. Thus, the sex chromosome effect on body weight is attributable to XX vs. XY differences in the number of X chromosomes. From Chen et al., 2012.