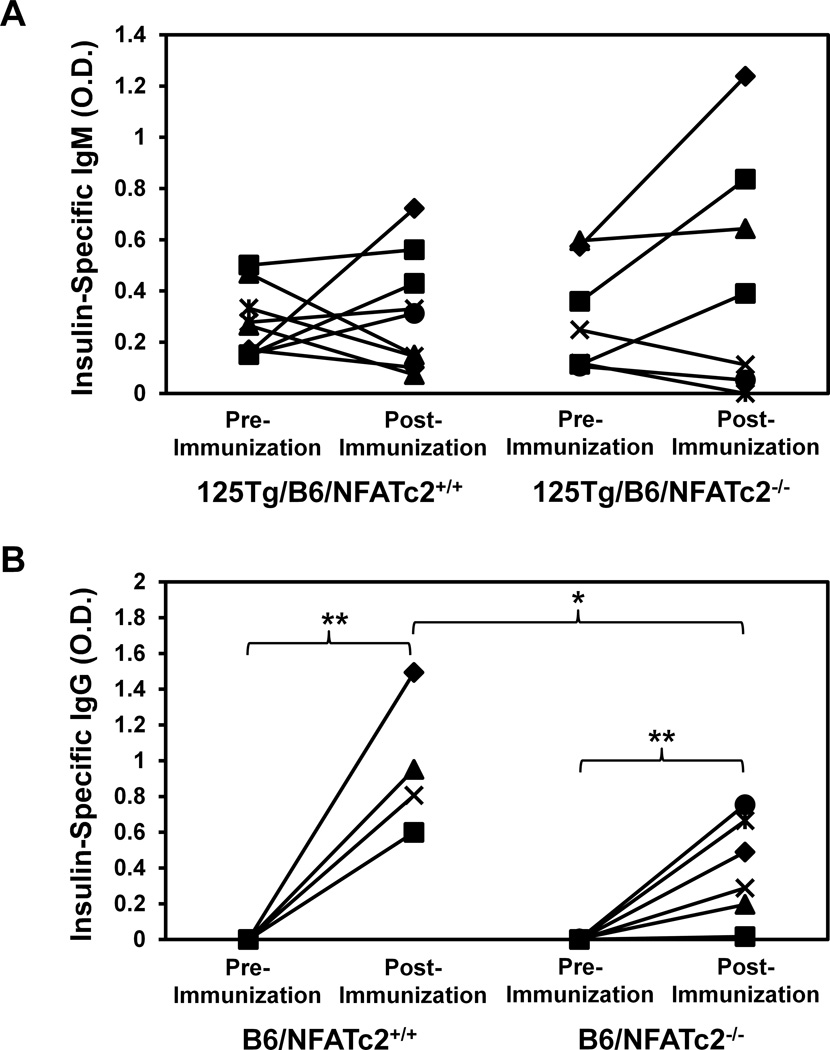
Figure 4. Functional inactivation of NFATc2 does not enhance insulin antibody production following T cell-dependent immunization.
Mice were immunized subcutaneously with beef insulin in CFA. Pre-immune and 2 weeks post-immunization sera were harvested and ELISA was used to measure the insulin-specific O.D. 405 nm as in Methods. (A) Pre-immunization and post-immunization IgM insulin-specific binding is compared in 125Tg/B6/NFATc2+/+ (left, n = 9) and 125Tg/B6/NFATc2−/− mice (right, n = 7). (B) Pre-immunization and post-immunization IgG insulin-specific binding is compared in B6/NFATc2+/+ (left, n = 4) and B6/NFATc2−/− mice (right, n = 6). Pre vs. post-immunization data were compared for each genotype, and pre (or post)- immunization was also compared between NFATc2−/− vs. NFATc2+/+ mice; * p = 0.05, ** p < 0.01 by two-tailed t-test;