Figure 1.
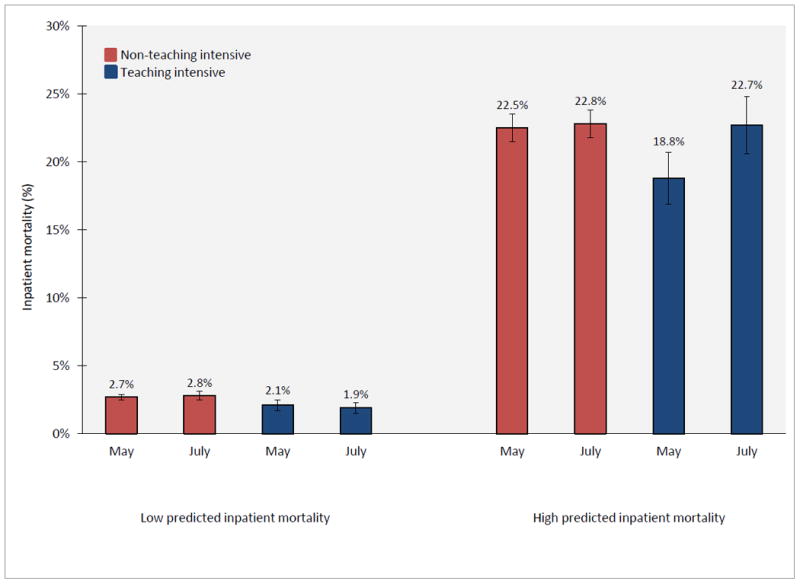
Adjusted inpatient mortality among patients admitted with AMI during May and July, according to teaching-intensive hospital status and predicted inpatient mortality risk. Adjusted inpatient mortality for teaching-intensive and non-teaching-intensive hospitals during May and July was estimated from a difference-in-difference logistic regression model which adjusted for patient age, sex, race, AHRQ predicted mortality, and year. The July mortality effect among high risk patients is (22.7 – 18.8) – (22.8 – 22.5) = 3.6 percentage points, p-value = 0.02. The July mortality effect among low risk patients is (1.9 – 2.1) – (2.8 – 2.7) = -0.3 percentage points, p-value = 0.24.
