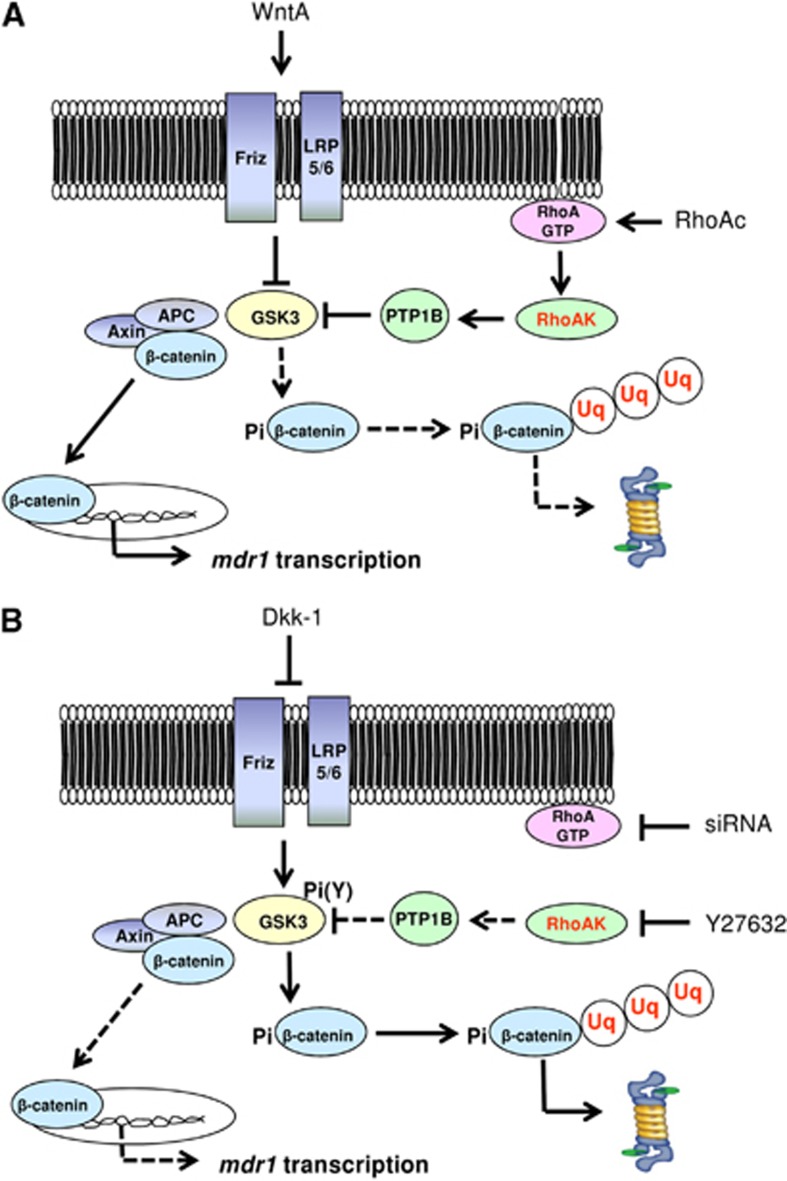
Figure 6.
Cross-talk between Wnt/GSK3 pathway and Wnt/RhoA/RhoA kinase (RhoAK) pathway and effects on P-glycoprotein (Pgp) expression in human blood–brain barrier (BBB) cells. (A) The Wnt activators (WntA) reduce the glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3)-mediated phosphorylation and ubiquitination of β-catenin, decreasing its proteasomal degradation. In these conditions, β-catenin is released from the APC/axin complex, translocates into the nucleus, and activates the transcription of mdr1 gene, which encodes for Pgp. The RhoA activation reduces as well the activity of GSK3: the active RhoA increases the activity of RhoAK, which induces the phosphorylation on serine 50 of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). After this phosphorylation, PTP1B dephosphorylates GSK3 on tyrosine 216 and inactivates it. Overall, the activation of the RhoA/RhoAK axis contributes to the transcription of β-catenin target genes, like mdr1. (B) The Wnt inhibitors (e.g., Dickkopf-1 (Dkk-1)) increase the GSK3-mediated phosphorylation and ubiquitination of β-catenin, priming it for the proteasomal degradation. The inhibition of RhoA (e.g., by RhoA small interfering RNA (siRNA)) or RhoAK (e.g., by Y27632) increases the GSK3 activity, by reducing the RhoAK-mediated phosphorylation of PTP1B on serine 50 and preventing the dephosphorylation of GSK3 on tyrosine 216. As a result, the nuclear translocation of β-catenin and its transcriptional activity are reduced, whereas the ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of β-catenin are increased. These data lead to hypothesize the existence of a cross-talk between the Wnt/GSK3 canonical pathway and the Wnt/RhoA/RhoAK non-canonical pathway in human BBB cells. APC, adenomatous polyposis coli; Friz, Frizzled; LRP5/6, low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 5/6; Pi, phosphate; Pi(Y), phosphotyrosine; RhoAc, RhoA activator II; RhoAK, RhoAK; Uq, ubiquitin. Continuous arrows indicate activated pathways; dotted arrows indicate inhibited pathways.