Figure 5.
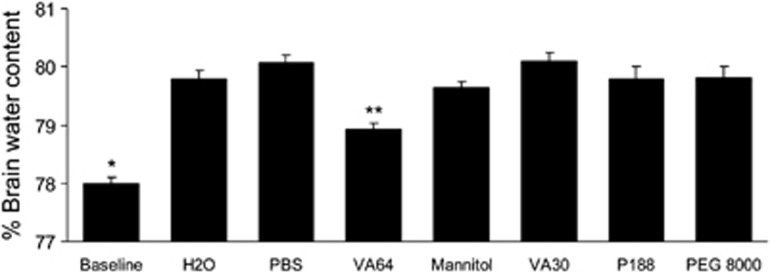
Effect of VA64 on cytotoxic brain edema after water intoxication. Mice were examined at baseline (n=9) or administered free water 200 mL/kg intraperitoneally (n=10) or free water plus VA64 (n=12) or other agents (mannitol, VA30, poloxamer P188, or PEG 8000; phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), n=5/group) intravenously (protocol 4). Brain water content was assessed at 1 hour. Compared with baseline values (normal brain), brain water content was significantly increased in all experimental conditions shown, including free water alone and PBS treatment (P<0.001, analysis of variance). VA64 significantly reduced brain water compared with PBS, mannitol, and all other treatments. *P<0.05 versus all other groups. **P<0.05 versus all other groups. PEG 8000, polyethylene glycol 8000.
