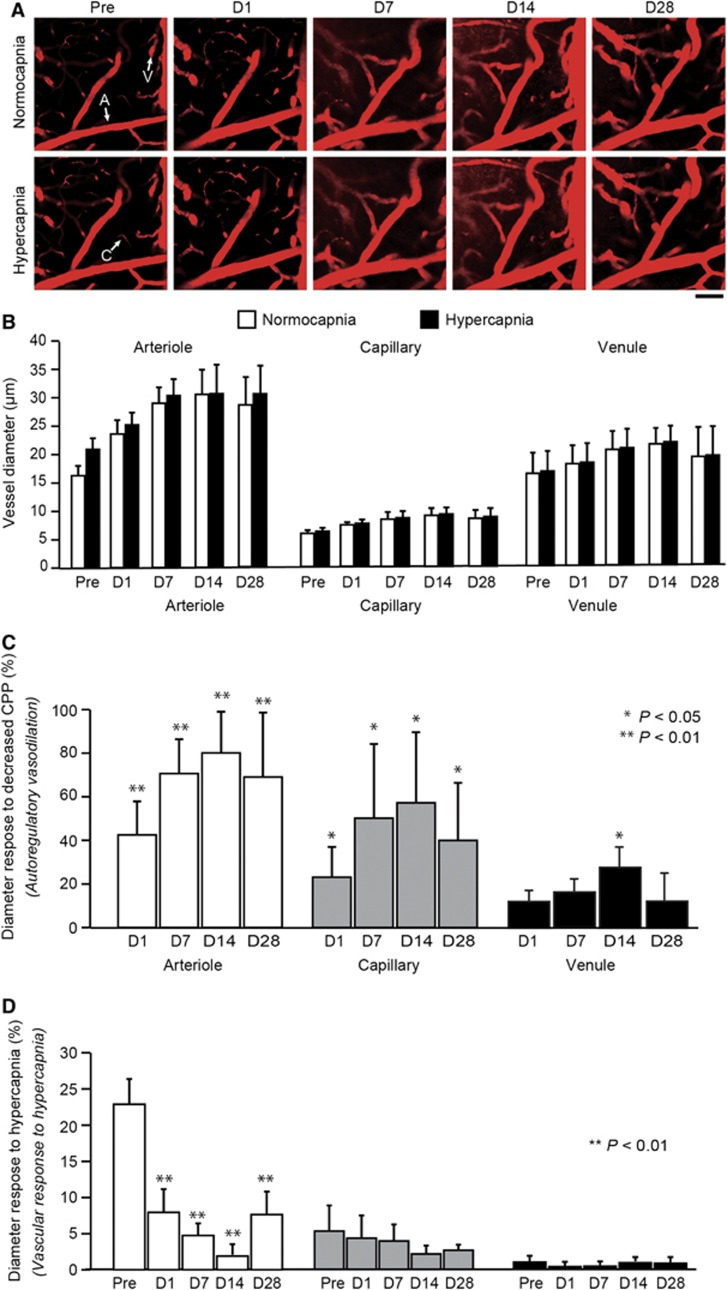
Figure 3.
(A) Longitudinal imaging of cortical vessels at the cortical surface in the hemisphere ipsilateral to unilateral common carotid artery occlusion (UCCAO). The arterioles are dilated significantly after UCCAO. Before UCCAO, the arterioles were dilated during hypercapnia. The dilation observed during hypercapnia was unnoticeable after UCCAO. Scale bar, 50 μm. (B) Longitudinal diameters in the cortical microvessels during normocapnia and hypercapnia in the hemisphere ipsilateral to UCCAO. (C) Longitudinal percentage changes in cortical microvessel diameter from the preoperative value. These findings represent the diameter response to decreased cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP; i.e., autoregulatory vasodilation). The microvessels dilated progressively and reached a maximum diameter at 14 days after UCCAO. (D) Longitudinal cortical microvessel diameter responses to hypercapnia. The diameter responses to hypercapnia in the arterioles were significantly decreased after UCCAO. The error bars indicate standard deviation. A, arteriole; C, capillary; V, venule. Normocapnia (white); hypercapnia (black). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (against preoperative value).