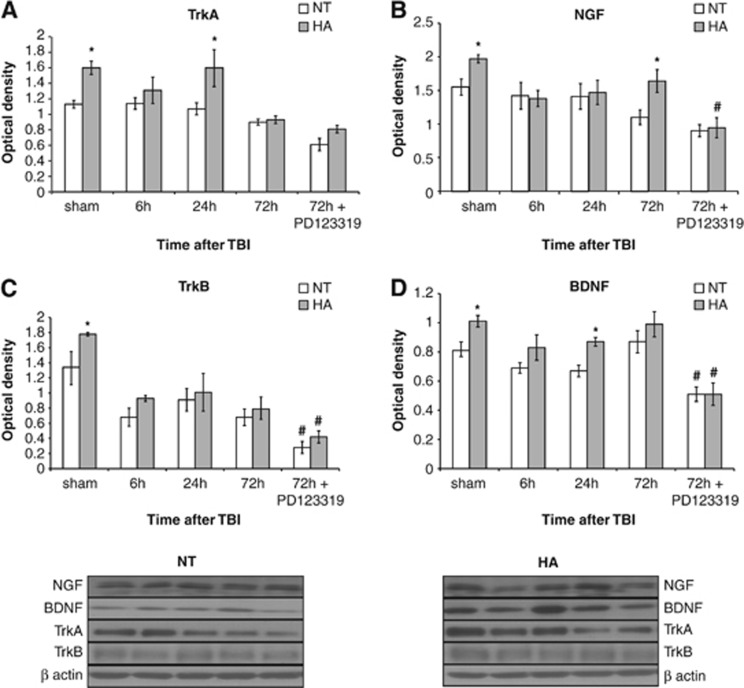
Figure 4.
Angiotensin receptor type 2 is involved in heat acclimation (HA)-mediated enhanced neurotrophin signaling. Mice were subjected to traumatic brain injury (TBI) after treatment with saline or PD123319 (PD, 10 mg/kg/day), and were killed at 6, 24, or 72 hours post TBI. HA elevated levels of tropomyosin-related kinase receptor A (TrkA, A) as well as its endogenous ligand, nerve growth factor (NGF). PD123319 treatment decreased NGF levels in HA mice (B). Elevated TrkB levels were seen in HA mice and were reduced after PD123319 treatment in both normothermic (NT) and HA mice (C). HA induced brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels, whereas PD123319 treatment reduced BDNF levels, in both NT and HA mice (D). *P<0.05 HA treated with saline versus NT treated with saline; #P<0.05 mice treated with saline versus mice treated with PD123319 of the same group (NT/HA), determined by two-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's test, n=6 per group.