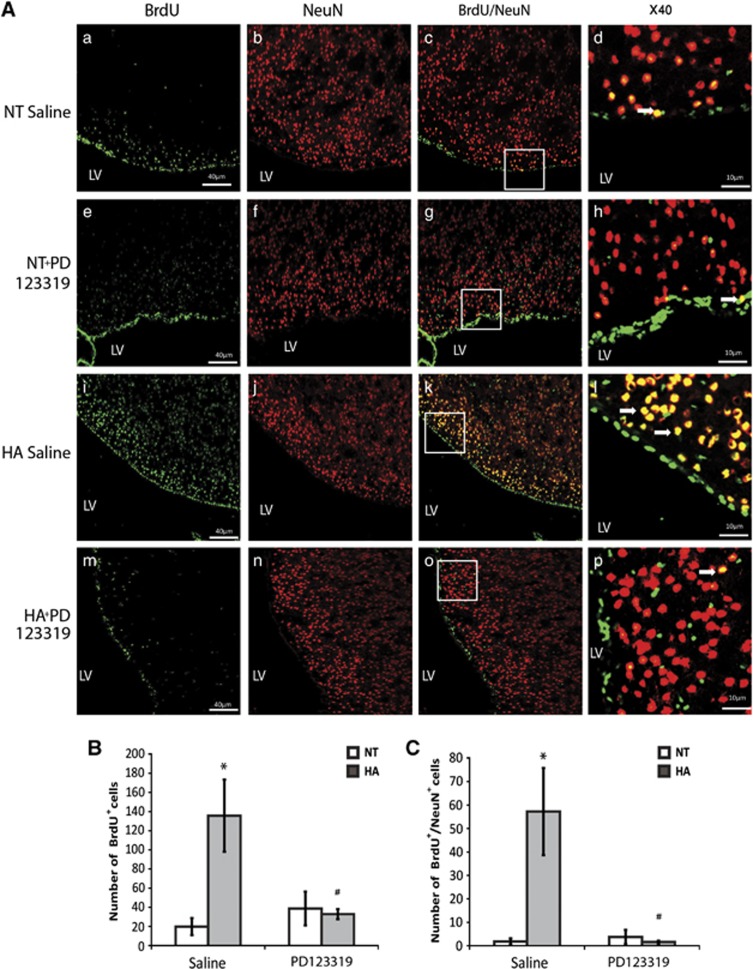
Figure 5.
Angiotensin receptor type 2 is involved in heat acclimation (HA)-mediated enhanced neurogenesis in the subventricular zone (SVZ). Mice were subjected to traumatic brain injury (TBI) after treatment with saline or PD123319 (PD, 10 mg/kg/day) for 3 days, and killed 42 days post TBI. Evenly sliced 10-μm sections were incubated with anti-NeuN for mature neurons and with anti-BrdU (anti-5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine) for newborn cells. (A) HA induced neurogenesis in the SVZ (i, j) and PD123319 (PD, 10 mg/kg/day) treatment blocked the observed neurogenesis (m–p). PD treatment (e–h) did not reduce neurogenesis in normothermic (NT) mice measured after saline treatment (a–d). Stereological quantification of the fields was used to count the number of BrdU-positive cells (BrdU+). Results show the average number of BrdU+ per field (B), and the average number of double-positive cells for NeuN and for BrdU (BrdU+/NeuN+) per field (C). *P<0.01 HA treated with saline versus NT treated with saline; #P<0.01 HA mice treated with saline versus HA mice treated with PD123319, determined by two-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey's test, n=6 per group.