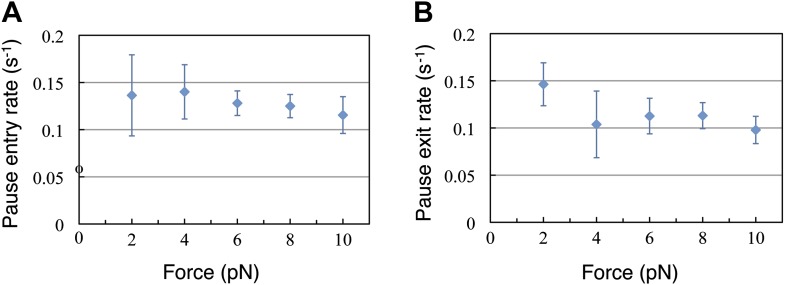
Figure 4. Pause entry and exit rates.
(A) Pause entry rate, calculated as the inverse of the mean duration of the translation bursts in between the pauses. (B) Pause exit rate, equal to the inverse of the mean pause duration. Both rates are essentially independent of the applied opposing force.