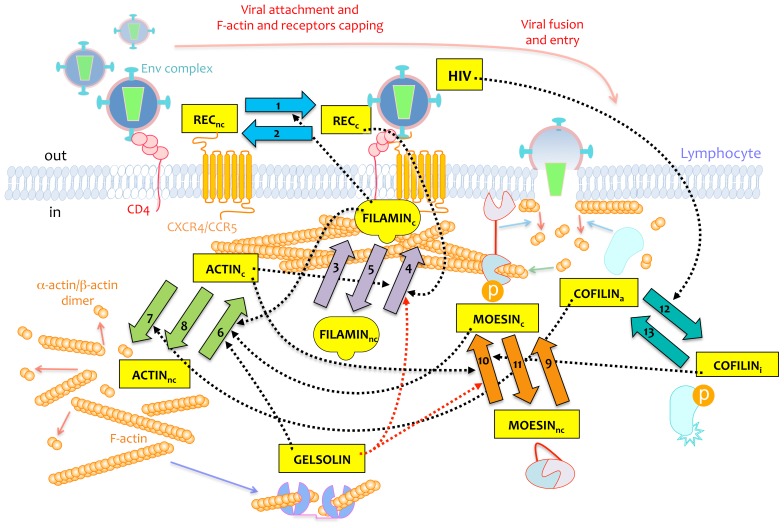
Figure 1. Representation of the molecular events simulated in the mathematical model.
Molecules included in the model as variables are the following: HIV, REC (CD4 and CXCR4 or CCR5 receptors for HIV-1 infection on lymphocyte cell-surface), FILAMIN, MOESIN (phosphorylated and active; dephosphorylated and non-active), COFILIN (a, active; i, inactive), and ACTIN. Molecules recruited at the HIV-1-triggered capping regions are indicated by the c subscript, while non-capped molecules outside this region are indicated by the nc subscript. As it is assumed that gelsolin remains constant during the whole process, it is not incorporated as a variable in the model. Numbered arrows (from 1 to 13) are the processes included in the model, and dashed arrows are the interactions from the molecules to the processes (black are positive, red are negative). Gelsolin acts by remodeling the amount and size of actin filaments, so the total amount of actin and its reorganization is reduced by higher expression of gelsolin (negative influence of GELSOLIN on processes 4 and 10, see Material and Methods for details); furthermore, appropriate levels of gelsolin facilitate, through the orchestrated severing and remodeling of actin filaments, the capping of actin filaments at viral entry regions (positive effect of GELSOLIN on process 6). Continuous arrows serve as an additional explanation of molecular events taking place during the invasion. Thus, red arrows represent depolymerization of actin filaments, blue arrows represent components which assist the depolymerization of actin filaments (e.g., active cofilin and inactivation of moesin in fusion pore formation), the green arrow indicates actin monomer incorporation to the growing actin filaments, and the purple arrow represents the actin severing and remodeling by gelsolin, thereby controlling the size of actin filaments and the amount of filaments reorganized to the viral entry regions on the plasma membrane of target cells.