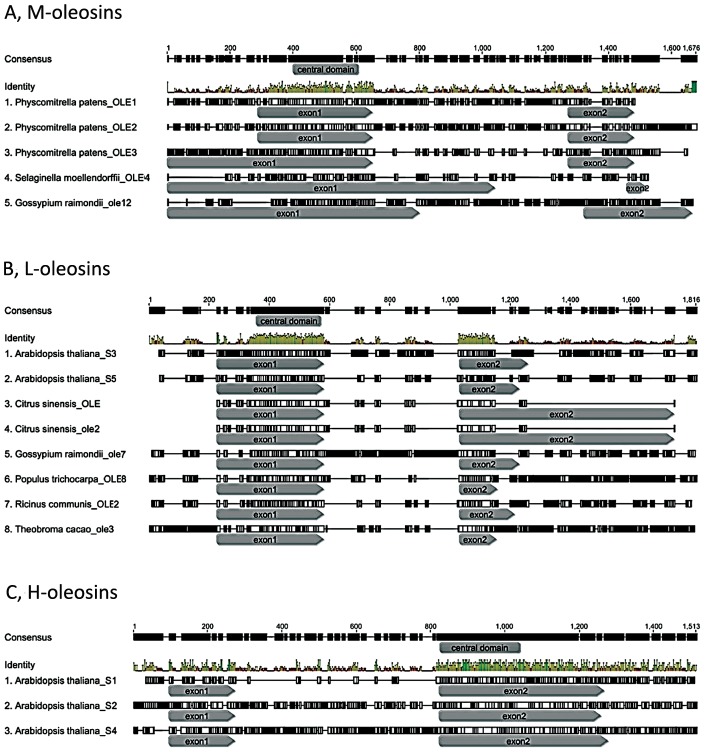
Figure 7. The intron position in each of the three oleosin isoforms.
At the nucleotide level, Joint Genome Institute database predict that most of oleosins possess no introns, whereas oleosin genes with intron insertion sites a single intron preceding or following the sequence encoding the central domain. The intron insertion sites are variable in oleosins, but nearly conserved within each isoform. The region of the central domain is labeled in the ‘consensus’ row. The intron positions are in between of the two encoding regions: exon1 and exon2. (A) M-oleosins; (B) L-oleosins; (C) H-oleosins.