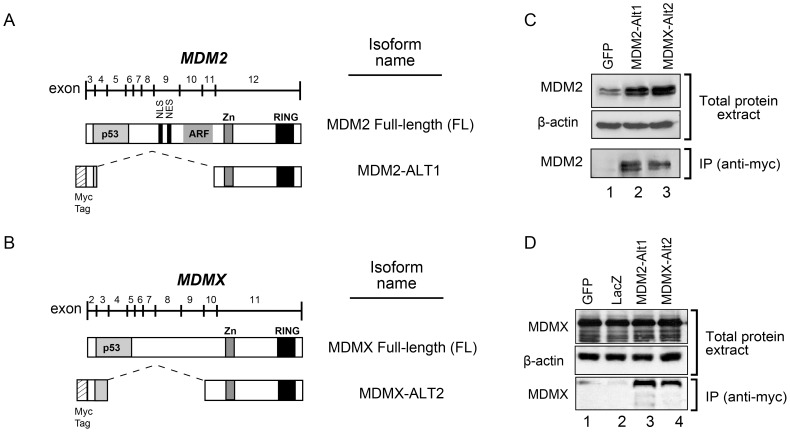
Figure 1. MDM2-ALT1 and MDMX-ALT2 interact with full-length MDM2 and MDMX.
A. Full-length MDM2 is encoded by exons 3 to 12 of the MDM2 gene and consists of the N-terminal p53-binding domain, the nuclear localization (NLS) and export signals (NES), the central ARF binding and Zinc finger domains and the C-terminal RING domain. MDM2-ALT1 comprises only exons 3 and 12 spliced together and the protein lacks the p53-binding domain. However, it retains the RING domain. B. Full-length MDMX, a close family member of MDM2, also comprises an N-terminal p53-binding domain, a central Zinc finger domain and a C-terminal RING domain and is encoded by exons 2 to 11 of the MDMX gene. MDMX-ALT2 consists of exons 2,3,10 and 11 and the protein is architecturally similar to MDM2-ALT1 in that it lacks the p53-binding domain but retains the RING domain. C. Myc-tagged constructs of LacZ, MDM2-ALT1 or MDMX-ALT2 were transfected into MCF7 cells. Immunoprecipitation of the myc-tagged proteins revealed the specific binding of full-length MDM2 to MDM2-ALT1 and MDMX-ALT2 and not to negative control protein myc-LacZ (compare lanes 2 and 3 to lane 1). Experiments were repeated a minimum of three times and consistent results were observed. Representative gel images are presented in the figure. D. Myc-tagged MDM2-ALT1 and MDMX-ALT2 co-immunoprecipitate with full-length MDMX while the negative control protein myc-LacZ does not interact with MDMX (compare lanes 2 and 3 to lane 1). These results were observed in two independent trials and representative images are shown.