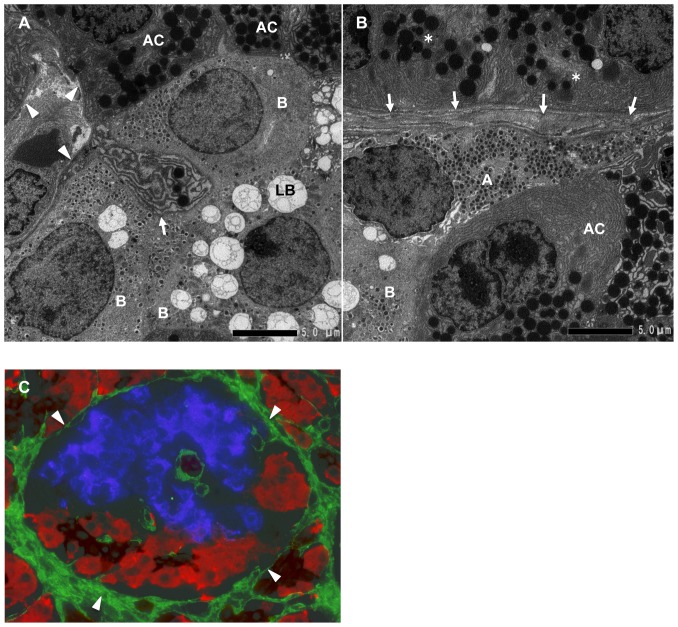
Figure 2. The interface between acinar-like cell clusters and islet cell clusters.
A: Magnified view of the interface between acinar-like cell clusters and islet cell clusters shown in Figure 1B (inset C). Acinar-like cells (AC) contact beta cells (B). Note that the acinar-like cell has a process (arrow) containing vesicles that protrude to the beta cell cytoplasm. BMs and ECM (arrowheads) surround beta cells (B) and acinar-like cells (AC). LB: lipofuscin body. B: Magnified view of the interface between acinar-like cell clusters and islet cell clusters shown in Figure 1B (inset D). Alpha cell (A) and beta cell (B) touching an acinar-like cell (AC) and the covering BMs and ECM (arrows) and pancreatic acinar cells (*) separated by BMs and ECM (arrows). C: Immunohistological demonstration of BMs and ECM stained for fibronectin (arrowheads, green), surrounding the islet beta cells stained for insulin (blue), and acinar-like cells (red) stained for amylase and the ductal marker cytokeratin 19 (brown).