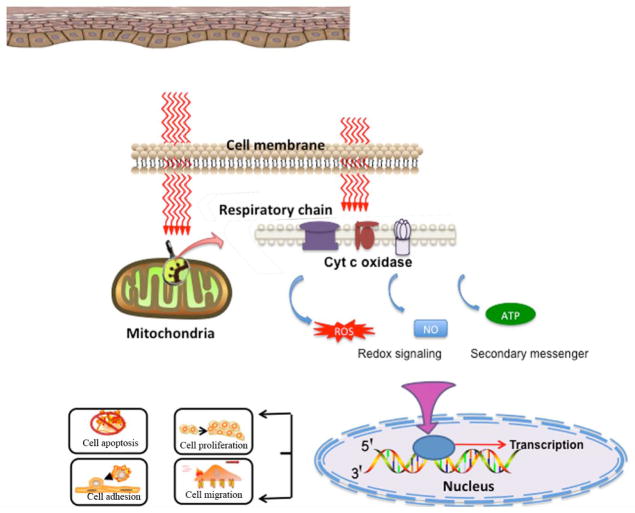
Figure 1.
Mechanism of action of LLLT.
Basic biological mechanism behind the effects of LLLT is thought to be through absorption of red and NIR light by mitochondrial chromophores, in particular cytochrome c oxidase (CCO) which is contained in the respiratory chain located within the mitochondria 5–7. It is hypothesized that this absorption of light energy may cause photodissociation of inhibitory nitric oxide from CCO 9 leading to enhancement of enzyme activity 10, electron transport 11, mitochondrial respiration and ATP production 12–14. In turn, LLLT by altering the cellular redox state can induce the activation of numerous intracellular signaling pathways; alter the affinity of transcription factors concerned with cell proliferation, survival, tissue repair and regeneration2,5,6,15,16.