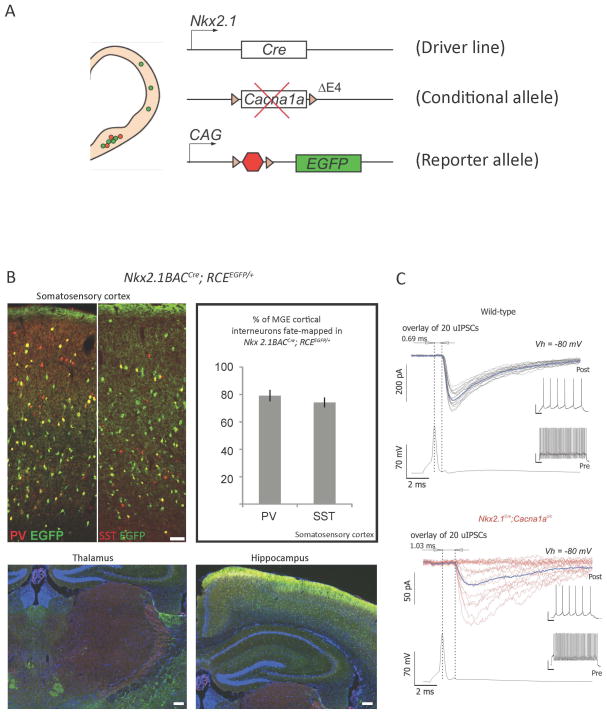
Figure 3. Conditional genetic strategies to generate mutant mice carrying cell-type selective mutations.
(A) Conditional genetic strategies allow the generation of mutant mice carrying a specific loss-of-function mutation in a gene of interest in a cell-type and tissue specific manner. Driver mouse lines are selected based on their expression of Cre recombinase driven by promoters expressed selectively in the cell-types and tissues of interest. This line is then bred on a conditional mutant mouse line carrying a floxed allele of the gene of interest, in which Lox P sites have been inserted around specific exons. The floxed allele is expressed properly in all tissues except in cells that express the Cre recombinase. In these mutated cells, the lox P sites will be recombined, effectively generating a deletion between the 2 sites, often leading to a loss-of-function allele. A conditonal reporter mouse line can be bred unto these mutants, allowing for the specific labeling of cells expressing the Cre recombinase. The mutated cells can then be tracked in a reliable fashion for their entire life-time as EGFP will be expressed stably over time. In the example illustrated here, an Nkx2.1Cre driver line was used to selectively ablate the 4th exon of the Cacna1a gene, leading to a loss-of-function allele. (B) The Nkx2.1Cre line was selected as it efficiently recombines the majority of cortical and limbic GABAergic interneurons derived form the medial ganglionic eminence, including the parvalbumin (PV) and the somatostatin (SST) expressing populations, while sparing the GABAergic cell populations in the thalamus reticular nucleus (RN). (C) Mutant cells can then be assessed using a variety of techniques, such as immunohistochemistry and in vitro physiology. In the example illustrated here, paired recordings between cortical fast-spiking (FS) GABAergic interneurons (identified using the RCEEGFP conditional labeling) and connected pyramidal cells revealed a significant alteration in the synaptic release properties of mutated FS interneurons in conditional Nkx2.1Cre; Cacna1ac/c;RCEEGFP mutant mice compared to littermate controls. These conditional mutants developed severe early-onset generalized seizures (adapted from Rossignol et al., Annals of Neurology, 2013).