Fig 1. The endostyle niche (EN).
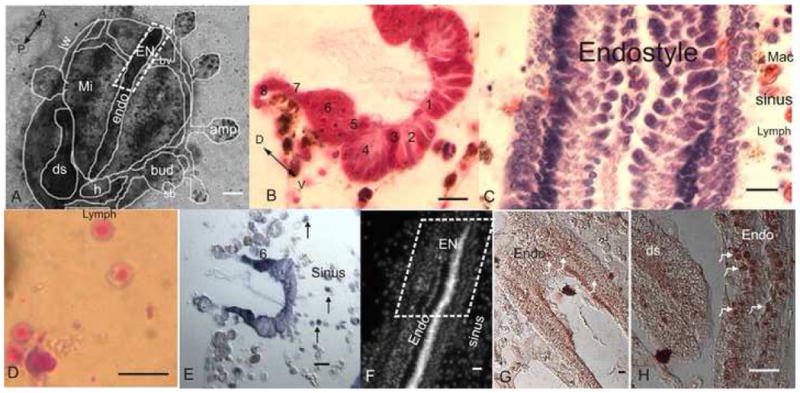
A. A microscopic ventral view of zooid buds and vasculature embedded in a tunic. The zooid endostyle bathes by cells that flow through its sinuses, with macrophages organized in islands next to it (role of macrophages in reutilization of materials in a new bud formation has been shown; Lauzon et al., 2002), digestive system and heart are located near its posterior end. EN is outlined at its anterior end. B. A cross section of the endostyle zones (1–8; azan heidenhain). C. A longitudinal section of the endostyle, lymphocyte cells and macrophages can be seen in its sinus (hematoxylin eosin). D. Potential stem cells, lymphocyte like cells which were drawn from the EN for the transplantation and labeling experiments, stained in May Grunwald Giemsa. E. Expression of Raldh (in dark purple) in the endostyle epithelial (higher at zone 6). Cells in the subendostylar sinus also express it (arrows) F. Nucleus location in the endostyle epithelial and sinus (Hoechst). G. Expression of PCNA in the endostyle (brown/arrows). H. Higher magnification of PCNA staining in the endostyle epithelial nucleus (arrows) andthe digestive system epithelial. endo-endostyle, EN-endostyle niche, sb-secondary bud, h-heart, ds-digestive system, amp-ampulla, mi-macrophage islands, bv-blood vessel, lw-lateral wall, A-anterior, P-posterior, D-dorsal, V-ventral, mac-macrophage, lymph-lymphocyte, numbers-zone number. scale bar A-100μm, B-H-10μm.
