Extended Data Figure 1. Assessing the fidelity and specificity of the Kit-Cre knock-in allele.
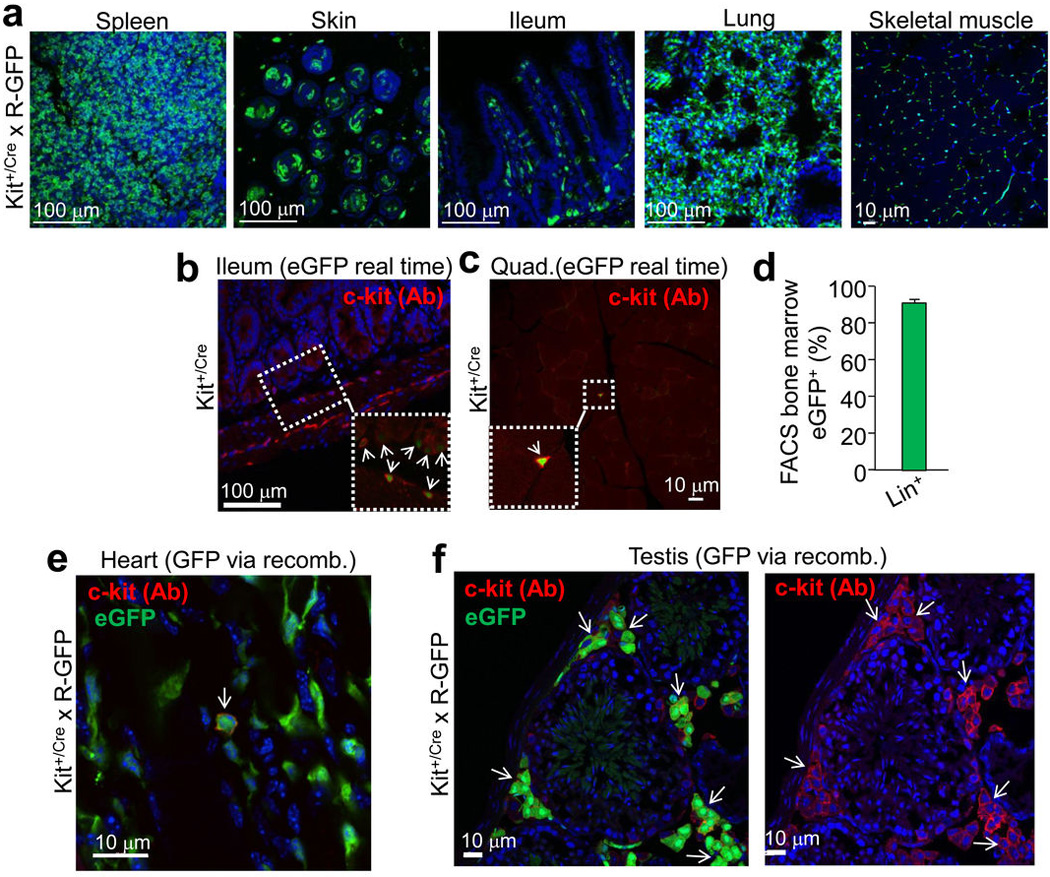
a, Histological sections from the indicated tissues of Kit+/Cre × R-GFP mice at 4 weeks of age. Blue is nuclei and green is eGFP. The data show eGFP expression in regions of each tissue that is often characteristic of endogenous c-kit protein expression. b, Immunohistochemistry for endogenous c-kit expression (red) in the mouse ileum at 4 weeks of age from Kit+/Cre mice that contain the IRES-eGFPnls cassette (but without the × R-GFP reporter allele) so that eGFP expression can be monitored in real time. The inset box and arrows show the co-staining with c-kit antibody and eGFP. c, Immunohistochemistry for endogenous c-kit expression (red) in quadriceps muscle of Kit+/Cre mice at 4 weeks of age versus nuclear eGFP (green) from the Kit+/Cre allele. While lineage tracing in Kit+/Cre × R-GFP mice, which is cumulative, showed abundant endothelial cells throughout the skeletal muscle (a), instantaneous c-kit expressing cells are rare in skeletal muscle, and when identified, are always mononuclear (inset box). d, FACS quantitation of bone marrow from Kit+/Cre × R-GFP mice at 4 weeks of age sorted for eGFP expression, of which 94% are positive for the “lineage” cocktail of differentiation-specific antibodies (n=3 mice). Hence the Kit-Cre allele is properly expressed in bone marrow and traces lineages that arise from c-kit+ progenitors. e, Immunohistochemistry in the hearts of Kit+/Cre × R-GFP mice for endogenous c-kit expression (red) versus all the cells that underwent recombination throughout development and the first 4 weeks of life, shown in green. While cells that are actively expressing c-kit protein are very rare in the heart (≈5 per heart section), the arrow shows such a cell that is also eGFP+ for recombination. All of the currently c-kit expressing cells identified in the heart were eGFP+, further verifying the fidelity of the Kit-Cre allele. f, Same experiment as in e except the testis was examined because of the characteristic pattern of Leydig cells that are known to be actively c-kit expressing cells. The data show that greater than 80% of the currently c-kit antibody reactive Leydig cells (red outline, better observed in the right panel) are also eGFP+ (arrows show clusters of these cells).
