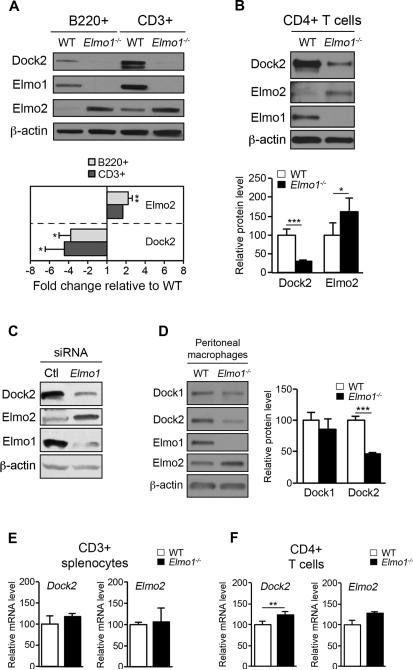
Figure 6. Elmo1 control of Dock2 levels in leukocytes.
(A) Splenocytes from WT and Elmo1−/− mice were FACS-sorted by anti-B220 and anti-CD3 staining, lysed and analyzed by IB with the antibodies indicated to the left. Graph (below) shows fold change in Dock2 and Elmo2 levels in Elmo1−/− cells relative to WT as determined by IB for n = 3 mice/genotype, ±SEM. (B) Splenic CD4+ T cells were analyzed by IB as in A. Graph (below) is average of n = 8 mice/genotype, ±SEM. (C) Jurkat cells transfected with a non-targeting control (Ctl) or Elmo1 targeting siRNA were analyzed by IB with indicated antibodies. (D) F4/80hi resident peritoneal macrophages were FACS-sorted from WT and Elmo1−/− mice and analyzed by IB with indicated antibodies. Graph to the right shows the relative levels of Dock1 and Dock2 in F4/80hi RPM for n = 4 mice/genotype, ±SEM. (E, F) qRT-PCR analysis of splenic CD3+ (E) and CD4+ T cells (F) for n = 3-5 mice/genotype, ±SEM.