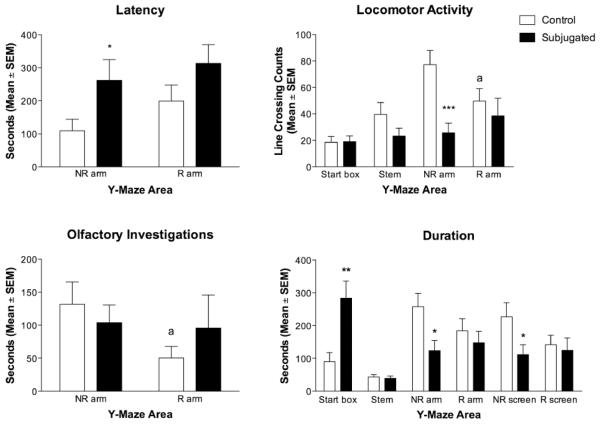
Figure 2.
Comparison between control and subjugated hamsters for different behavioral measures (Mean ± SEM) performed in each section of the Y-maze: start box, stem, arm with non- receptive female (NR Arm), arm with the receptive female (R Arm), proximity of the screen by the non receptive female (NR Screen), and proximity of screen by the receptive female (R Screen). The behaviors included duration of time in section of the maze, latency to enter the arms of the maze, locomotor activity (expressed as lines crossed), and duration of time spent performing olfactory investigations. Subjugated hamsters were exposed daily to aggressive males from postnatal day 28 (P-28) to P-42, while Controls were placed in empty clean cages. All tests were conducted at mid-puberty on P-45. Groups were compared for each section of the maze (Student t-tests; * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001). Comparisons were also made between R and NR arms within the groups (Paired t-tests, a p<0.05).