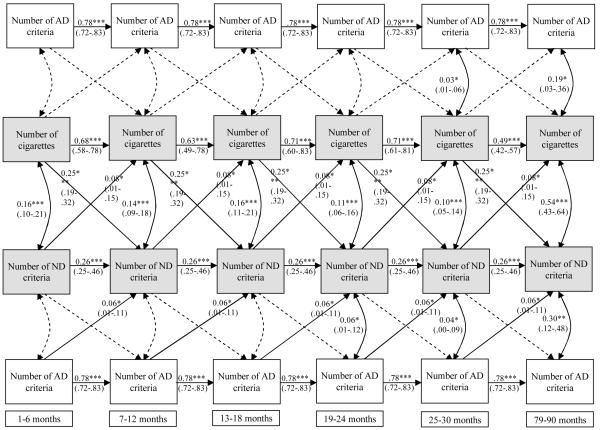
Figure 2.
Autoregressive cross-lagged model of cigarette consumption, DSM-IV nicotine dependence (ND) criteria and alcohol dependence (AD) criteria over a seven-year period after smoking onset (N=409)
Note. Model controls for five time-constant variables (sex race/ethnicity, onset age of smoking, pleasant initial sensitivity to tobacco, parent smoking/nicotine dependence) on the two smoking phenotypes and two time-constant variables (sex, race/ethnicity) on the alcohol phenotype. The alcohol phenotype was included as a time-varying cross-lagged bi-directional predictor of the two smoking phenotypes simultaneously and is presented twice in the figure to avoid cluttering of arrows. Unstandardized coefficients and 95% confidence intervals are shown. Dotted paths are not significant.
N free parameters = 99; Log likelihood = −5494.76; BIC = 11584.87; CFI = 0.81; RMSEA = 0.09
*p<.05; **p<.01; ***p<.001