Fig. 2.
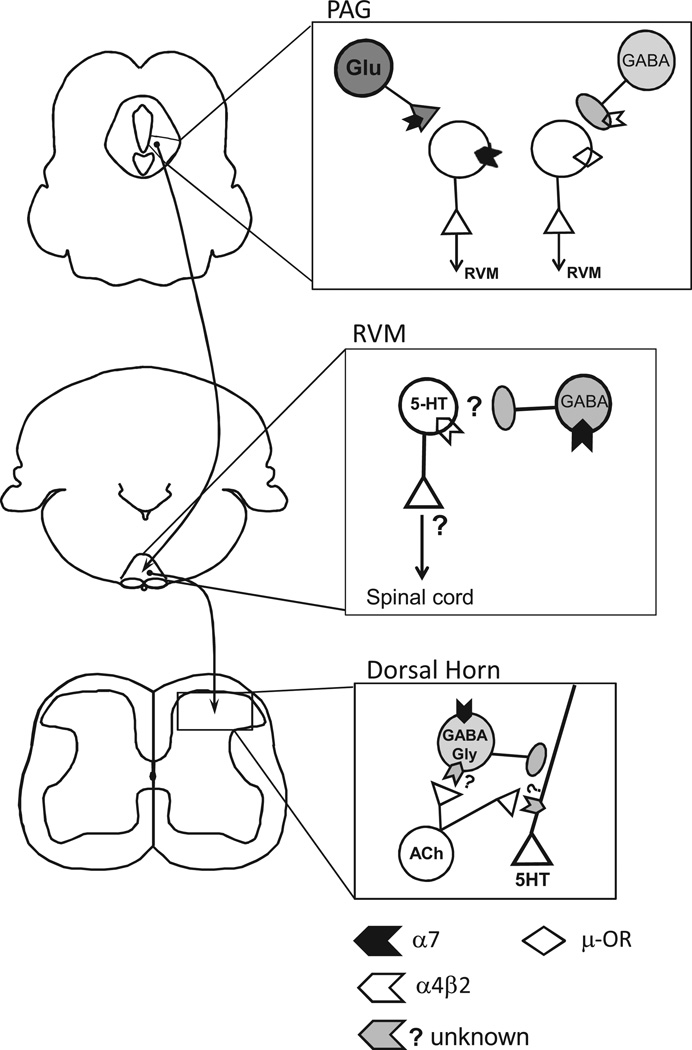
Nicotinic receptors modulate descending pain modulatory pathways. PAG:Our recent finding sindicate that a subset of ventrolateral PAG(vlPAG) neurons express α7 nAChRs on their somata (α7),and that this population was distinct from neurons that express µ-opioid receptors (µ-OR). Specifically, 50% (33/69) of vlPAG projection neurons responded to acetylcholine (ACh). Responses were blocked by the α7-selective antagonist MLA (n = 15). In a separate experiment, we observed 4 response classes among vlPAG projection neurons: nAChR-only responses (8/41). µ-OR– response accompanied by weak/no nAChR response (13/41), both nAChR and µ-OR responses (4/41), or no response of either type(16/41) (unpublished observations). In addition, activation of presynaptic α7 nAChRs increased glutamatergic drive to nAChR+neurons that project to the RVM. By contrast, nicotine-induced modulation of GABAergic inputs to nAChR+vlPAG projection neurons was rare. In the right panel, we hypothesize that presynaptic nAChRs modulate inhibitory drive to a majority of vlPAG projection neurons that lack the somatic nAChR. The presynaptic nAChR that mediates this phenomenon has not been characterized but is likely to be α4β2, based on previous work in the PAG [92]. We propose that presynaptic and somatic α7 nAChRs contribute to excitation of putative pain-inhibiting neurons in the vlPAG. This could be a supraspinal mechanism for α7 nAChR-mediated analgesia. RVM: Although the RVM is a well-documented site for supraspinal analgesia, the underlying circuitry is still not well-understood. Immunohistochemistry studies show that α4β2 nAChR subtype and 5-HT markers are co-localized [83]. However, electrophysiological approaches have not verified this finding. In addition, the specific projection targets of α4β2-containing 5HT RVM neurons are not known, particularly within the context of descending pain modulatory pathways. α7 nAChRs are expressed on GABA interneurons in the RVM [86]. Although the RVM is implicated in nicotinic analgesia via behavioral studies, more work is needed to investigate the cellular mechanisms at the circuit level. Spinal Dorsal Horn: Tonic endogenous cholinergic tone modulates serotonin release from descending inputs, which is mediated by nAChRs that are neither α4β2 nor α7. These receptors are located on descending serotonergic inputs, as well as on neighboring GABAergic interneurons that make axo-axonic contacts with serotonergic terminals. Additional modulation of 5HT release via a non-tonic mechanism is mediated by α7 nAChRs located on the somata of GABAergic interneurons that make axo-axonic contacts with descending serotonergic input. The impact of this modulation on nociception in normal or pathological states needs further investigation (modified from [42]).