Figure 3.
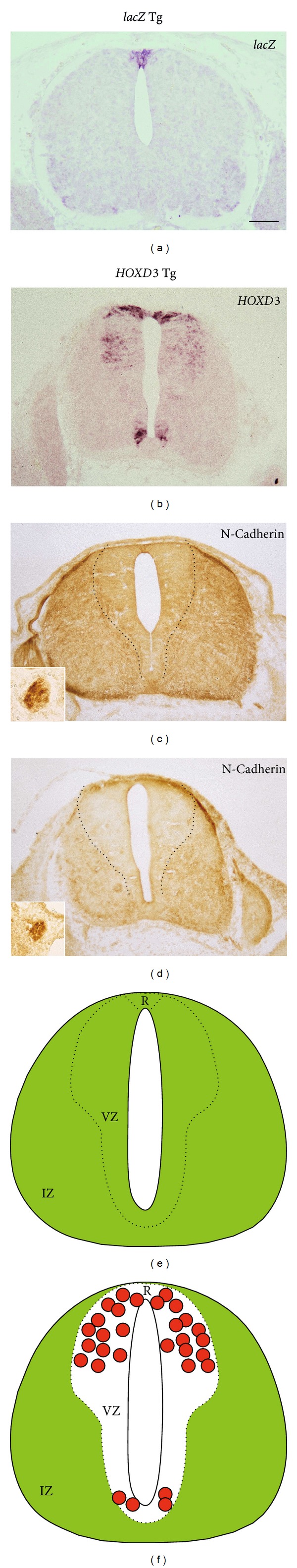
Reduced N-cadherin expression induced by HOXD3 overexpression in the roof plate of the early mouse embryo. (a, b) Expression of lacZ and HOXD3 genes in transverse neural tube sections at the thoracic level of 12.5-day transgenic embryos. Transgenic embryos were generated, in which lacZ and HOXD3 are expressed in the roof plate cells under the control of the Wnt1 regulatory element [34]. These embryos were sectioned and analyzed using in situ hybridization. Expression of lacZ (control) is restricted to roof plate cells within the neural tube, while HOXD3 expression is localized not only in the dorsal neural tube, but also within the ventricular zone and in ventral regions of the neural tube. (c, d) N-Cadherin expression in the thoracic neural tubes of 12.5-day lacZ- and HOXD3-expressing transgenic embryos. Transverse sections were stained using anti-human N-cadherin antibodies [34]. N-Cadherin is strongly expressed in the ventricular zone of lacZ-expressing embryos, whereas the ventricular zone in HOXD3-expressing embryos is composed of a number of progenitor cells that do not express N-cadherin. The ventricular zone is surrounded by dotted lines. Insets show that N-cadherin expression levels in the sympathetic ganglia of lacZ-expressing embryos are similar to those of HOXD3-expressing embryos. (e, f) Summary of the neural tube phenotype in transgenic embryos expressing lacZ and HOXD3. In embryos expressing lacZ, N-cadherin expression (green) is distributed throughout the neural tube. In HOXD3-expressing embryos, roof plate cells expressing HOXD3 (red circles) expand ventrally into the ventricular zone, where almost all N-cadherin-expressing cells are lost. R, roof plate; IZ, intermediate zone; VZ, ventricular zone. Scale bar: 100 μm.
