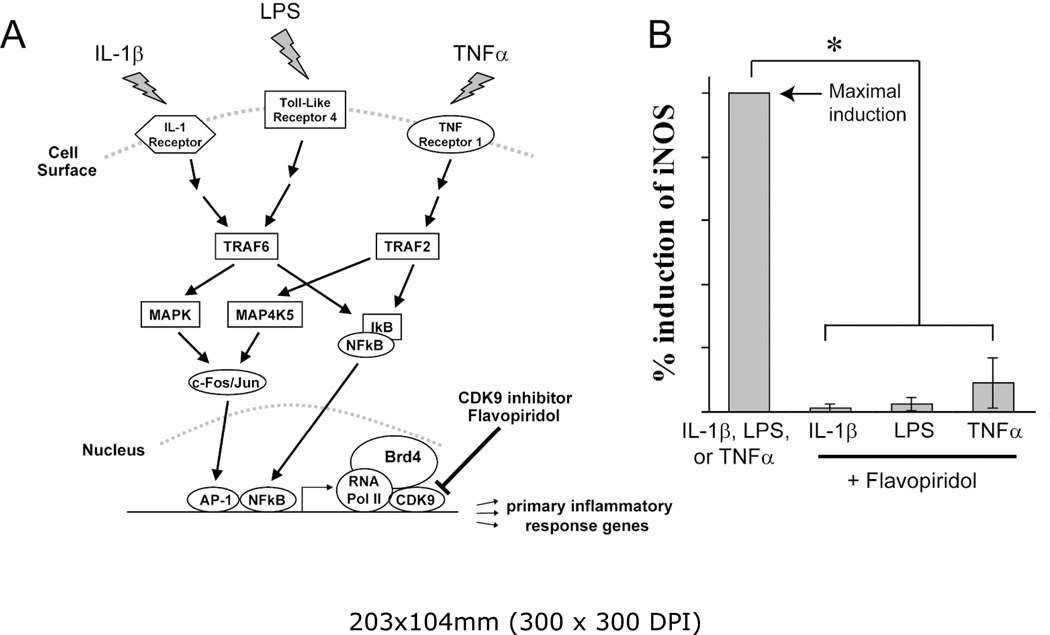
Figure 2. The CDK9 inhibitor Flavopiridol is effective against different inflammatory stimuli.
(A) Activation of inflammatory genes by diverse signals. Multiple pro-inflammatory stimuli, such as IL-1β, LPS, and TNFα activate their respective cell surface receptors. These signals are then transmitted through different intracellular mediators/pathways, which ultimately converge on CDK9-dependent transcription of inflammatory genes. Brd4 functions to recruit CDK9 to activated promoters. (B) Flavopiridol is effective against multiple inflammatory stimuli. Human chondrocytes (n=3 different donors) in monolayer culture were treated with different inflammatory stimuli (10ng/ml of either IL-1β, LPS, or TNFα) with or without 300 nM Flavopiridol for 5 hours. iNOS mRNA was quantified by real-time PCR as a measure of inflammatory response. The induction of iNOS by each stimulus alone was arbitrarily set to 100% (first bar) and compared to the respective value obtained in sample co-treated with each inflammatory stimulus and Flavopiridol. Results were the mean +/− standard deviation from three different donors (*p<0.05).