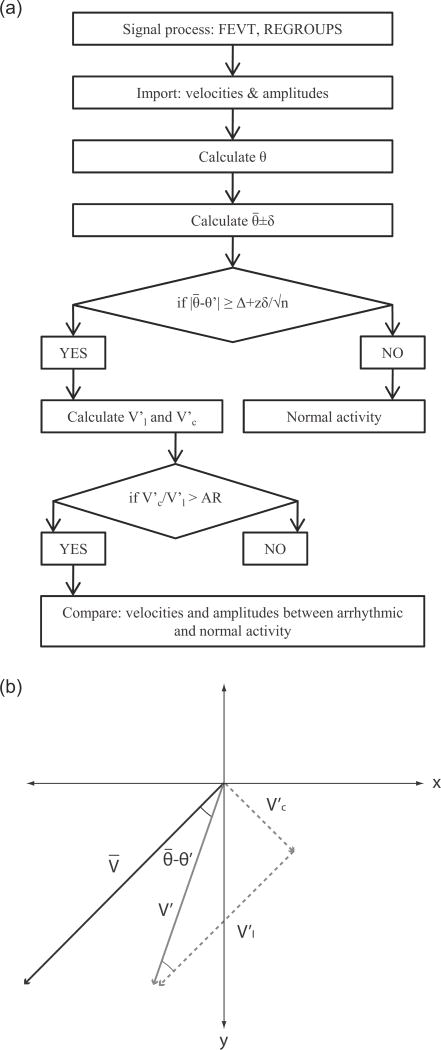
Fig. 1.
Arrhythmic slow wave identification. (a) Flowchart of the identification algorithm. The orientation of the velocity was used as the indicator of arrhythmia. The angle of each velocity (θ) and the average angle of the normal activities ( ) was calculated. The standard-error-mean was calculated from the standard deviation (δ), number of events (n), and the z-value at 95% confidence interval. The threshold value was calculated by adding an offset value (Δ) to the standard-error-mean. (b) An identified arrhythmic velocity (V′) was decomposed into a longitudinal component ( ) and a circumferential component ( ), with the longitudinal direction defined by the direction of the normal velocity (V).