Figure 1.
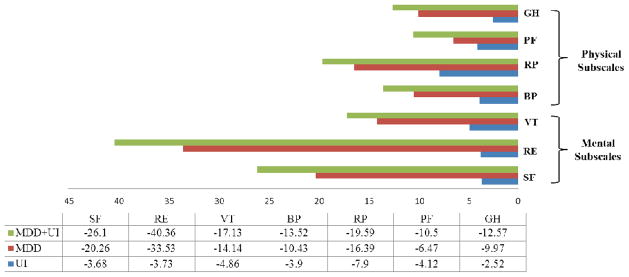
Decrements in physical and mental HRQOL subscalesa associated with urinary incontinence (UI), major depressive disorder (MDD) and coexisting MDD and UI among Medicare beneficiaries, adjusting for demographics and comorbid conditionsb.
aBP= bodily pain; RP= role-physical; PF= physical functioning; GH= general health; SF= social functioning; RE= role-emotional; VT=vitality
bDemographics and comorbidities adjustment set (index, referent): age at survey (65–74, 75–84, 85+), smoker (yes, no), race (other, white), gender (male, female), marital status (other, married), education (> high school, ≤ high school), high blood pressure, stroke, chronic lung disease (includes COPD, emphysema or asthma), gastrointestinal problems (including Crone’s, ulcerative colitis, or inflammatory bowel disease) diabetes, difficulty completing one or more activities (getting out of chair, use of toilet, walking, eating, dressing, bathing), joint pain, cardiovascular disease
