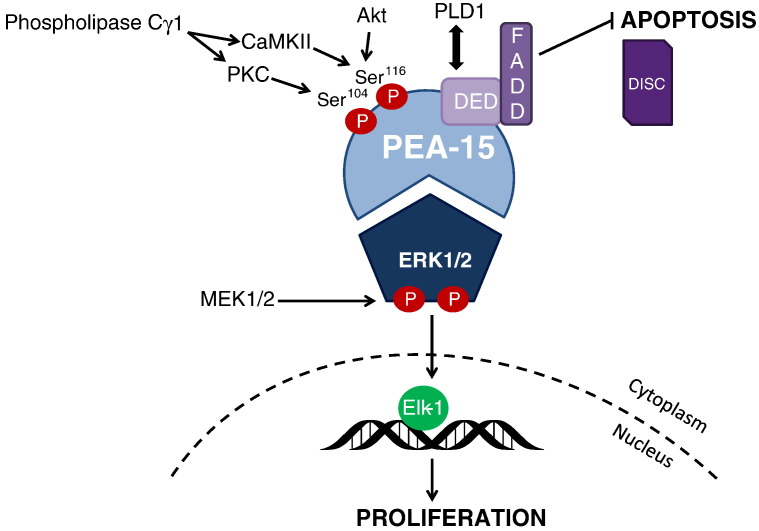
Fig. 1.
The role of PEA-15 in proliferation and apoptosis. PEA-15 has two phosphorylation sites which are preferentially phosphorylated by PKC at Ser104 and CaMKII or Akt at Ser116. PKC and CaMKII can both be activated by phospholipase Cγ1. PEA-15 is an ERK1/2 binding protein and acts as an “anchor” of ERK1/2 by sequestering it in the cytoplasm, preventing subsequent translocation into the nucleus. PEA-15 can bind both ERK1/2 and phosphorylated ERK1/2 with equal affinity which is activated by the upstream MAP kinase kinase, MEK1/2. Phosphorylation of PEA-15 releases ERK1/2 resulting in the activation of the nuclear transcription factor, Elk-1 and proliferation of the cell. PEA-15 contains a DED which upon phosphorylation promotes the binding of FADD. The association of PEA-15 and FADD prevents FADD-mediated activation of caspases and the formation of the DISC resulting in an inhibition of apoptosis. The DED of PEA-15 also interacts with PLD1.