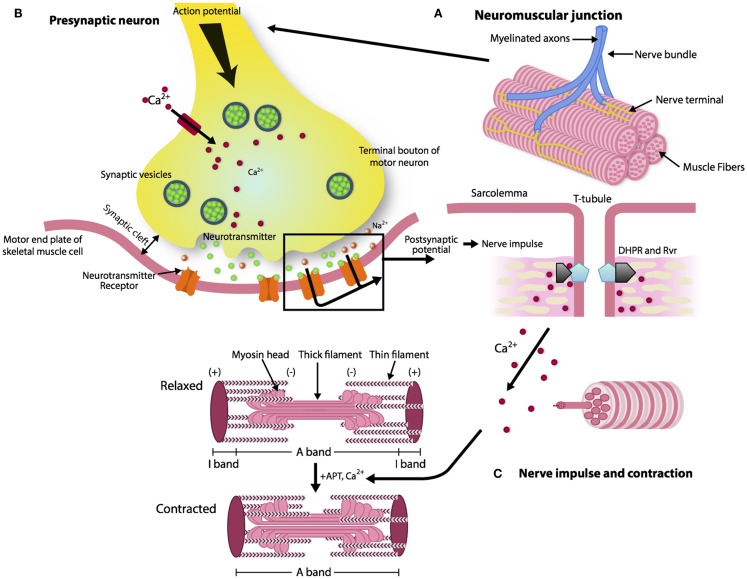
Figure 1.
The architecture of a neuromuscular junction (NMJ). (A, B) The NMJ is composed of three elements: pre-synaptic (motor nerve terminal), intrasynaptic (synaptic basal lamina), and post-synaptic component (muscle fiber and muscle membrane) (Punga and Ruegg, 2012). When the action potential reaches the motor nerve terminal the calcium channels open and the calcium enters in the neuron and delivers ACh in the synaptic cleft. (C) AChR activates the DHPRs located in the sarcolemma and by induction the RyRs. Calcium released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum through the RyRs binds to troponin C and allows cross-bridge cycling and force production.