Figure 4. Dermal DCs (DDCs) are closely associated with cutaneous nerves and depend on NaV1.8+ nociceptors for IMQ induced IL-23 production.
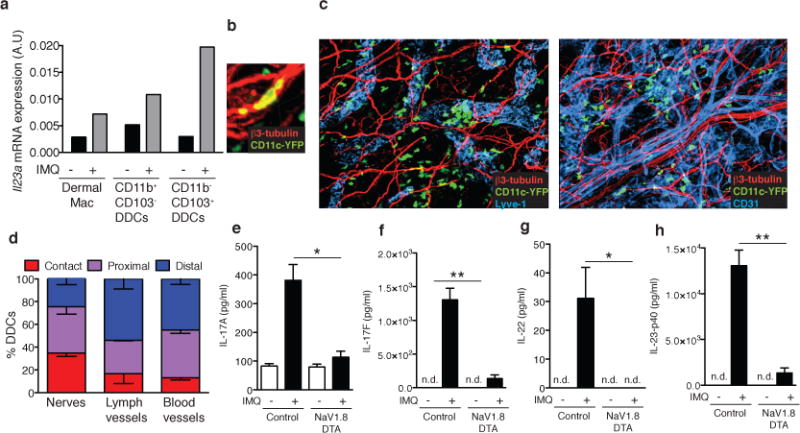
a, Mice were challenged with IMQ (n=20 pooled mice/condition) and after 6h, myeloid cell populations comprising dermal macrophages and two subsets of DDCs were FACS sorted (Extended Data Fig. 8c) from cell suspensions to measure il23a mRNA by qPCR. b, Representative confocal micrographs of ear skin whole mounts from CD11c-YFP mice stained for β3-tubulin (peripheral nerves, red) and Lyve-1 (collecting lymphatics, blue) or CD31 (blood and lymphatic endothelial cells, blue). Original magnification was 200X. c, Close-up confocal micrograph of a CD11c-YFP cell in contact with a nerve (see also Suppl. Videos 1&2). d, Quantification of 3D DDC proximity to peripheral nerves, lymphatics, and blood vessels in normal ear skin. The frequency of DDCs (n=330) in contact, proximal (0–7μm) and distal (>7μm) to nerve fibers was determined as described in Methods and a Chi-square test showed bias of DDC to nerves relative to lymphatics and blood vessels (***P< 0.0001).e–h, Ears of NaV1.8-DTA or control littermates were treated daily with IMQ. Total protein was prepared from ear skin after 3 days and (e) IL-17A, (f) IL-17F, (g) IL-22 and (h) IL-23p40 were quantified by ELISA (n=4 ears/condition; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).
