Fig. 6.
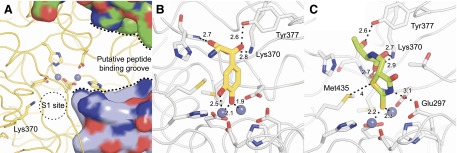
Modeling of selected inhibitors in the DNPEP active site. (A) Structure of the DNPEP active site (PDB accession code 3VAT) showing the binuclear zinc center (gray spheres) in relation to the S1 site and the peptide-binding groove of the enzyme, which is partially formed by additional subunits of the DNPEP complex (shown in surface representation). Lys370, present in the S1 site of the enzyme, confers selectivity by interacting with the negatively charged N-terminal Asp or Glu residue of DNPEP peptide substrates. Models of (B) compound 241320 and (C) compound 347749 binding to the DNPEP active site. The model in (B) was docked based on the structure of methionine aminopeptidase in complex with a catechol-containing inhibitor (Wang et al., 2008), whereas the model in (C) was placed assuming that the exocyclic double-bonded sulfur atom is the relevant metal chelator in this compound. Both models were energy minimized using the Crystallography and NMR System program (Brunger, 2007). Distances are given in angstroms.
