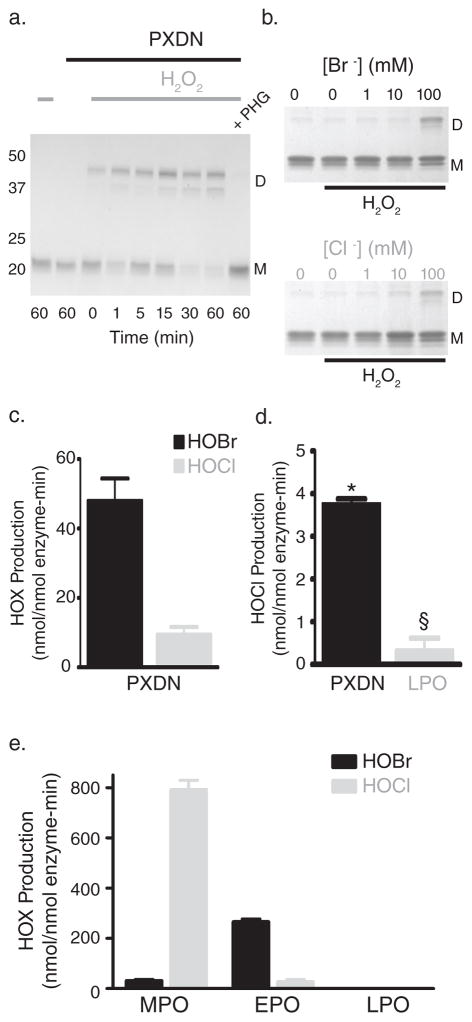
Figure 3. Peroxidasin forms hypohalous acids and sulfilimine bonds in collagen IV.
(a) SDS-PAGE of reactions consisting of 16 nM purified human peroxidasin, 500 nM monomeric NC1 hexamer (3 μM potential cross-links), and 10 μM H2O2 in 1X PBS. Control reactions without H2O2 or in the presence of the peroxidase inhibitor, phloroglucinol (PHG; 50 μM), were also conducted. D represents cross-linked dimeric NC1 subunits, while M denotes uncross-linked monomeric subunits. (b) Coomassie stained gel after SDS-PAGE of collagen IV NC1 hexamer is shown to illustrate relative amounts of sulfilimine cross-linked dimeric (D) and uncross-linked monomeric (M) subunits after incubation of uncross-linked PFHR-9 basement membranes in varying buffer halide concentrations (Br− or Cl− as K+ salt) with or without 1 mM H2O2. (c) Peroxidasin (PXDN) mediated hypohalous acid (HOX) production expressed as nmol hypohalous acid generated per nmol enzyme per minute measured in 1X PBS + 100 μM NaBr. Values represent mean ± s.e.m. (n=3). (d) HOCl production measured directly in 1X PBS without added Br−. Values denote mean ± s.e.m. (n=4). PXDN mediated HOCl generation was significantly greater than LPO (*unpaired two-tailed t-test, p < 0.05), while LPO was not statistically different from zero (§ one sample t-test, p = 0.32). (e) Hypohalous acid (HOX) production in nmol hypohalous acid generated per nmol enzyme per minute for myeloperoxidase (MPO), eosinophil peroxidase (EPO), and lactoperoxidase (LPO) in 1X PBS + 100 μM NaBr. Values represent mean ± s.e.m. (n=3). Full gel images are displayed in Supplementary Fig. 14.