Figure 3.
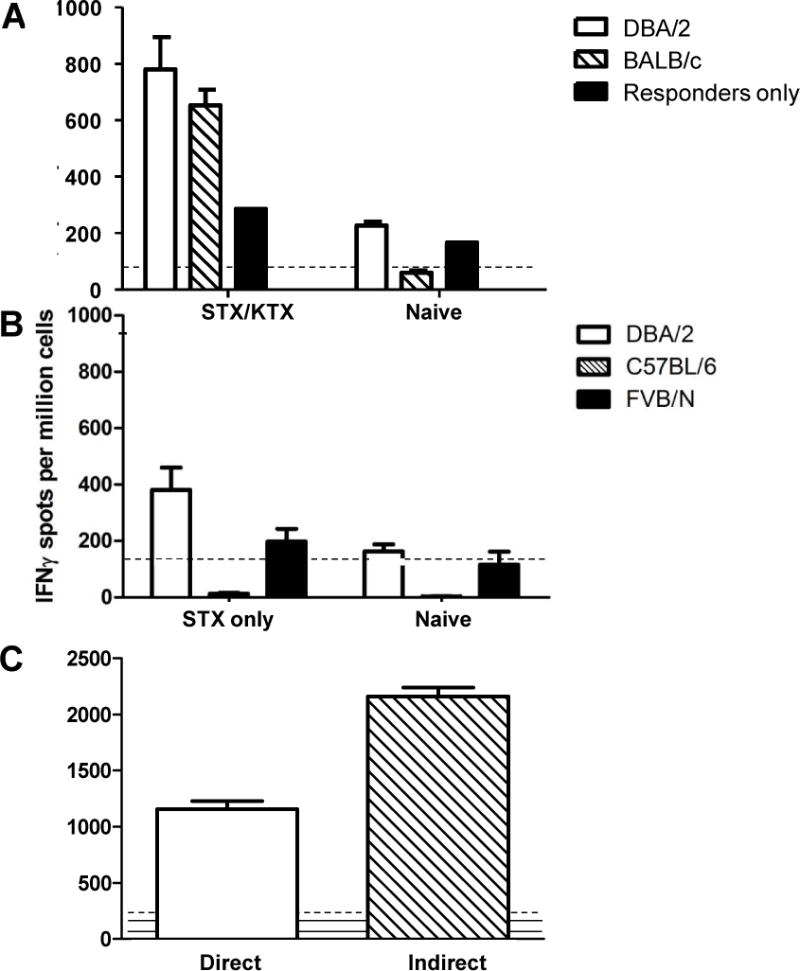
Sensitization to donor alloantigens followed by renal transplantation increases the frequency of donor-reactive CD4 T cells. A. Purified splenic CD4 T cells from B6 hosts that had rejected both renal and skin allografts from DBA/2 donors (STX/RTX) or from naïve recipients (Naïve) were tested in an IFNG ELISPOT assay against the indicated targets. B. Purified splenic CD4 T cells from B6 hosts that had rejected DBA/2 skin allografts only (STX only) or from normal B6 hosts (Naïve) were tested in an IFNG ELISPOT assay for reactivity to B6 (syngeneic), DBA/2 (allogeneic), or FVB/N (third party) SC targets. C. Unseparated SC from primed B6 hosts at the time of rejection of DBA/2 renal allografts were tested in an IFNG ELISPOT assay against either intact (direct) or subcellular (indirect) irradiated stimulator cells. Data shown are the mean (+ SEM) IFNG spots per million cells. Dashed lines show reactivity of stimulators only; solid lines show reactivity of responders only.
