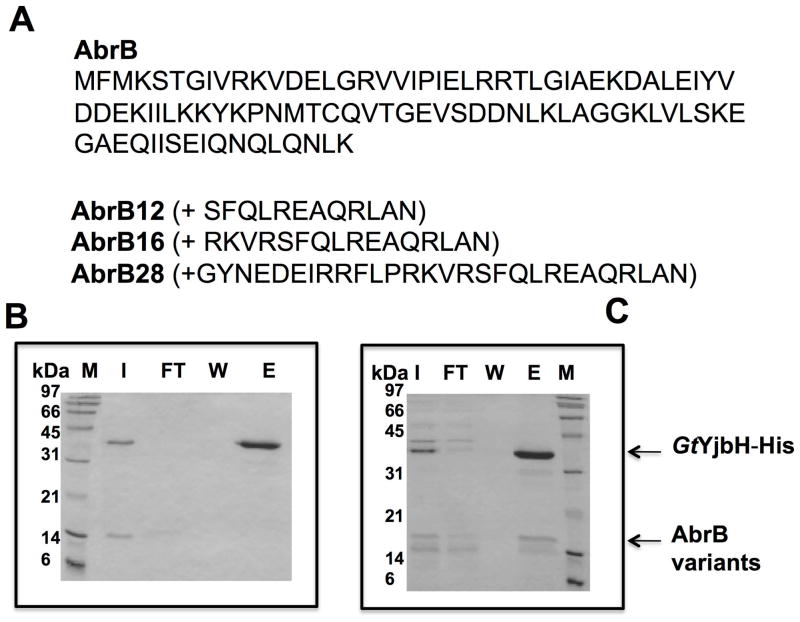
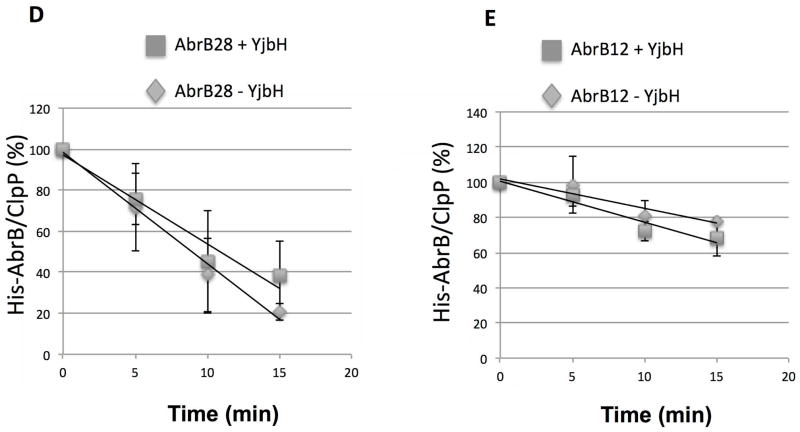
Fig. 2. The 28 residues from Spx C-terminal region are sufficient for YjbH interaction and ClpXP proteolysis.
A. Chimeric protein sequences of AbrB12, AbrB16, and AbrB28 were constructed by fusing the coding sequence of abrB with the last 12, 16, and 28 codons of spx, respectively.
B and C. In vitro Ni affinity pull-down experiments to detect interaction between GtYjbH-His6 and AbrB12 or AbrB28. Binding reactions contained 2.5 μM of each protein, and were incubated at room temperature for 10 min. M, marker; FT, flow-through; W, wash; E, elution (Experimental Procedures for details). Binding data for GtYjbH and AbrB16 in supplemental Fig. S2.
D and E. In vitro proteolysis assay of AbrB28 (D) and AbrB12 (E) in the presence and absence of GtYjbH-His6. AbrB12 or AbrB28 (8 μM), ClpX (3 μM), and ClpP (8 μM) with an ATP-generating system (creatine kinase) were incubated at 37 °C for the times (min) indicated (left). The intensities of ClpP protein in each lane were used as internal controls (Zhang & Zuber, 2007). Plots of time course experiments showing AbrB28 and AbrB12 decay in proteolysis reactions containing ClpXP with (2.6 μM) and without YjbH. Data are from 3–4 replicate reactions with error bars showing standard deviation. Trend-lines were generated with Excel and used to calculate time point at which 50% of substrate was degraded (T50).