Fig. 5.
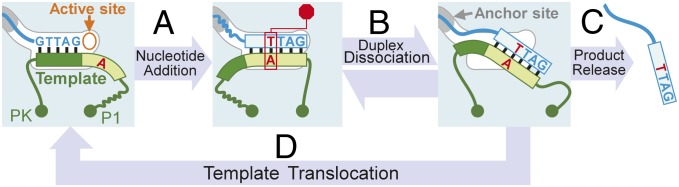
A model of the telomerase sequence-defined catalytic cycle. A duplex formed from the RNA template and DNA primer is bound to the telomerase active site. Nucleotide addition (step A) proceeds, specified by the template sequence. After addition of three nucleotides past the pause signal (red), nucleotide addition is arrested. Duplex disassociation (step B) leads to an unbound duplex with DNA 5′ overhang bound to the TERT anchor site. The strand separation of RNA/DNA duplex results in either complete DNA product release (step C) or template translocation (step D) that aligns and regenerates the duplex bound by the active site, which is ready for further nucleotide addition (return to step A).
