Figure 1. Robo2 and hb9 mutants have similar motor axon guidance defects, and hb9 is required for robo2 expression in the RP motor neurons.
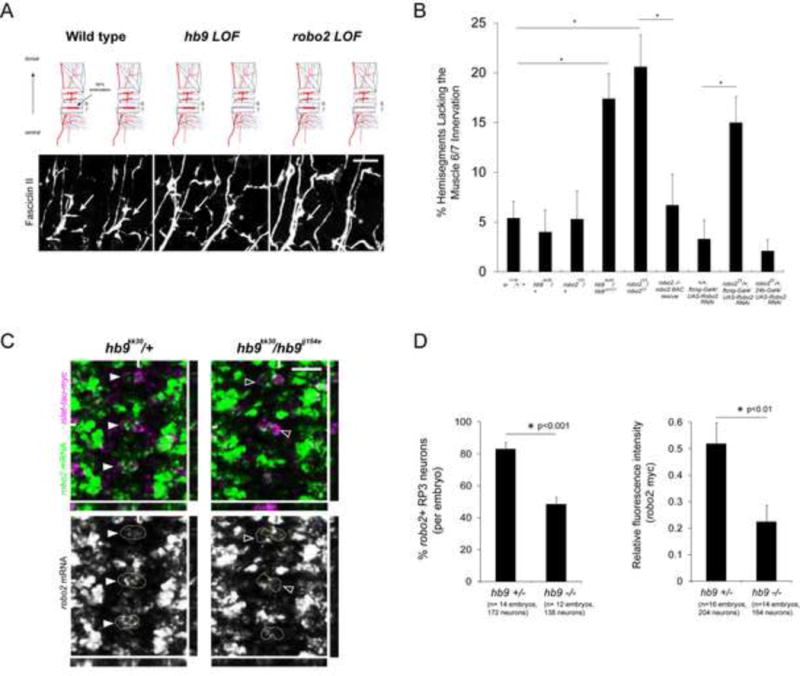
A: Stage 17 embryos stained for Fasciclin II (FasII). Anterior is left. Arrows point to the muscle 6/7 innervation, which is often absent in hb9 or robo2 mutants (asterisks). B: The percentage of hemisegments lacking the 6/7 innervation is shown; asterisks indicate a significant difference (Student’s t-test, p<0.01). Error bars = s.e.m. C: Fluorescent in situ for robo2 mRNA in Stage 16 embryos. Anterior is up. The RP3 motor neurons are labeled by the islet-tau-myc transgene, and circled in the single-channel images. Most RP3 neurons express robo2 in hb9 heterozygotes (filled arrowheads), whereas many RP3 neurons do not express robo2 in hb9 mutants (empty arrowheads). YZ and XZ cross-sections are shown; hash marks indicate the planes of the sections. D, Left: RP3 neurons were scored as positive or negative for robo2. Hb9 mutants have significantly fewer robo2+ RP3 neurons than heterozygous siblings (Student’s t-test, p<0.001). Error bars = s.e.m. D, Right: The mean gray value of the robo2 mRNA signal in RP3 neurons was normalized to the mean gray value of the myc signal. The average relative fluorescence intensity of robo2 mRNA is significantly lower in hb9 mutants than in hb9 heterozygotes (Student’s t-test, p<0.01). Error bars = s.e.m. Numbers of embryos and neurons analyzed are shown in parentheses. Scale bars represent 10 μm. Robo2 −/− robo2 BAC rescue denotes robo2123, 22K18robo2BAC/ robo233. Hb9 +/− denotes hb9kk30, isl-taumyc/TM3. Hb9 −/− denotes hb9kk30, isl-taumyc/hb9jj154e. See also Figure S1.
