Figure 2. Restoring Robo2 activity in hb9 mutants rescues motor axon guidance defects.
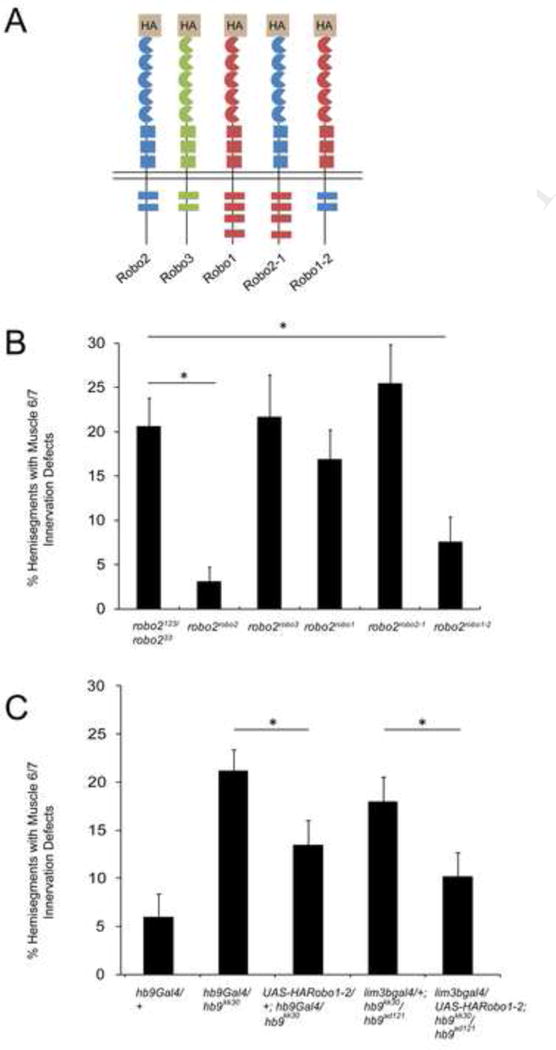
A: Schematic of the Robo receptors analyzed for their ability to replace endogenous Robo2. B: Embryos homozygous for knock-in alleles in which the coding sequences of Robo2, Robo3, Robo1, Robo2-1, or Robo1-2 are inserted in the robo2 locus were analyzed for motor axon guidance defects. Only Robo2 and Robo1-2 can restore muscle 6/7 innervation. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (Student’s t-test, p<0.01). Error bars = s.e.m. B: Hb9 mutant embryos over-expressing UAS-HARobo1-2 have fewer defects than mutants lacking the transgene (Student’s t-test, p<0.05). All hb9 mutants were scored blind to genotype. Error bars = s.e.m. See also Figure S2.
