Figure 3. Hb9’s Eh domain is required for its activity in motor axon guidance and for robo2 regulation.
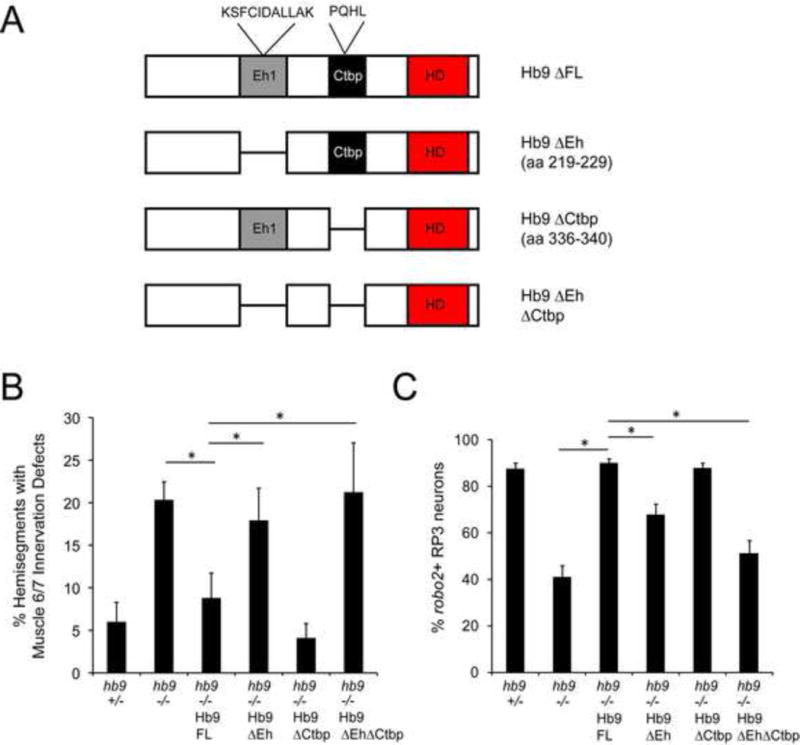
A: Schematic of the Hb9 variants analyzed for their ability to rescue hb9 mutants. B: Muscle 6/7 innervation was quantified in late Stage 17 embryos; asterisks indicate a significant difference (Student’s t-test, p<0.01). Hb9 transgenes lacking the Eh domain failed to rescue motor axon guidance defects in hb9 mutants. C: The percentage of robo2+ RP3 neurons per embryo is shown; asterisks indicate a significant difference (Student’s t-test, p<0.01). Hb9’s Eh domain is required for rescue of robo2 expression. Error bars = s.e.m. Hb9 +/− denotes hb9gal4/TM3. Hb9 −/− denotes hb9gal4/hb9kk30. Hb9 −/− Hb9 (variant) denotes UAS-Hb9 (variant)/+; hb9gal4/hb9kk30.
