Figure 5. The lateral position of hb9Gal4-expressing axons is disrupted in the absence of hb9, robo2, or robo3.
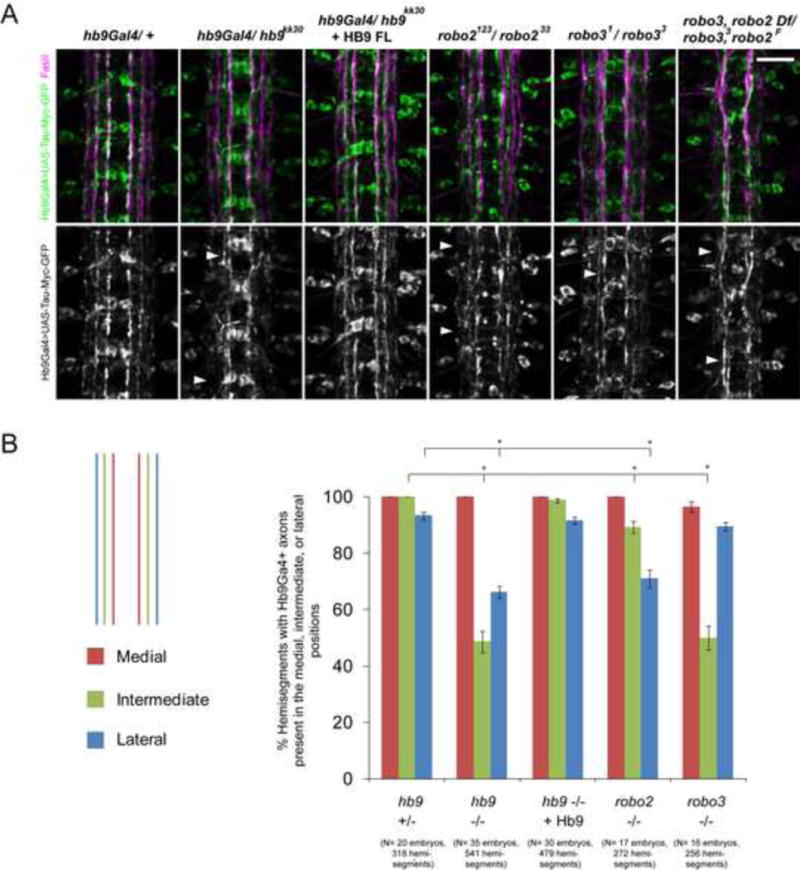
A: Stage 17 embryos, anterior is up. FasII staining is shown in magenta. Hb9Gal4> UAS-TauMycGFP (green) labels axons that form three bundles on each side of the midline in hb9 heterozygotes. In hb9 mutants, the outer hb9Gal4+ pathways are disrupted or shifted medially (arrowheads). Robo2 and robo3 mutants partially phenocopy these defects (arrowheads). B: The percentage of hemisegments containing hb9Gal4+ axons in the medial, intermediate, or lateral positions is shown. Asterisks indicate a significant difference (Student’s t-test, p<0.001). Error bars = s.e.m. Numbers of embryos and hemisegments scored are shown in parentheses. Scale bars represent 10 μm. Hb9 +/− denotes hb9gal4/TM6B. Hb9 −/− denotes hb9gal4/hb9kk30. Hb9 −/− + HB9 denotes UAS-Hb9/+; hb9gal4/hb9kk30. Robo2 −/− denotes robo2123/robo233; hb9gal4/+. Robo3 −/− denotes robo31 / robo33; hb9gal4/+. Robo3, robo2 Df/ robo33, robo2F denotes Df(2L)ED108/ robo2F, robo33; hb9gal4/+. See also Figure S4.
