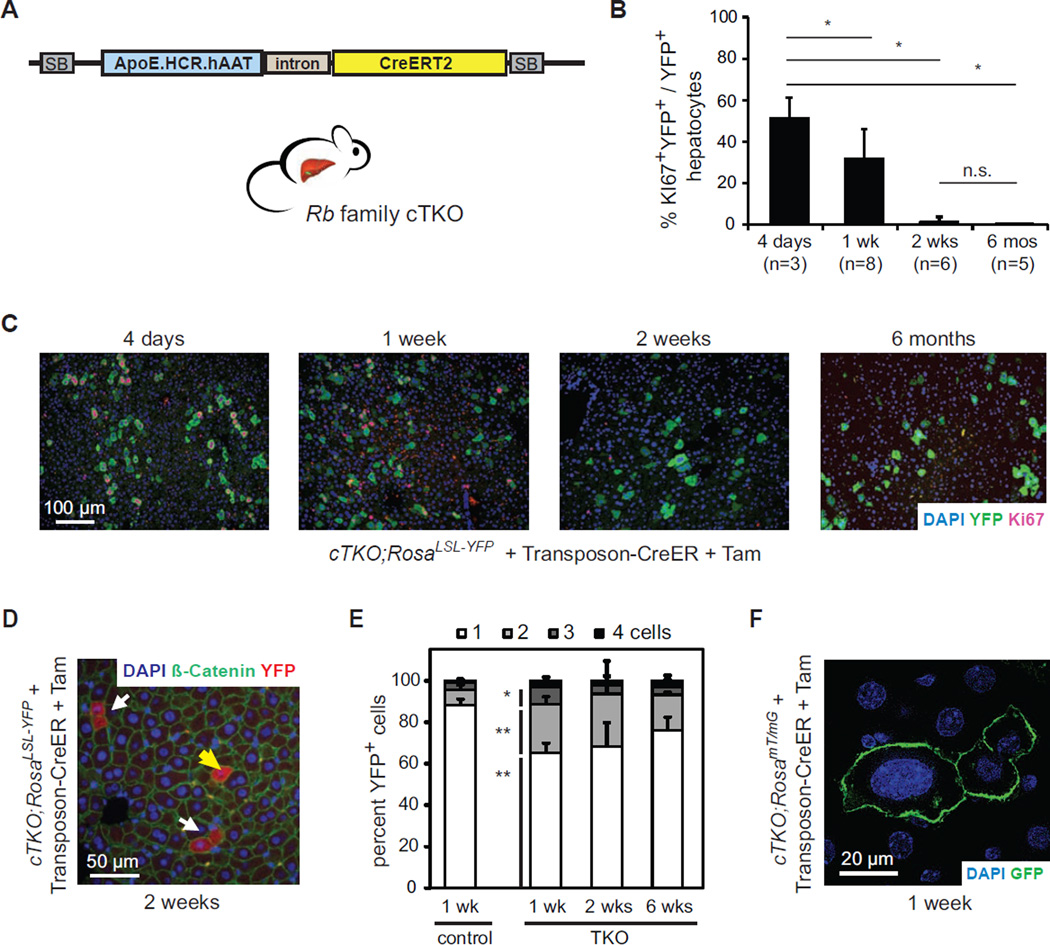
Figure 1. Rb pathway inactivation leads to transient cell cycle entry in hepatocytes.
(A)Schematic representation of the Sleeping Beauty (SB) Transposon-CreER system. ApoE.HCR.hAAT drives the expression of CreERT2 specifically in hepatocytes. (B and C) Acute Cre-mediated Rb gene family deletion in adult hepatocytes leads to cell cycle entry followed by cell cycle arrest. (B) Quantification and (C) representative images of Ki67+ cells (red) after Cre activation in transfected hepatocytes (YFP+, green) in cTKO;RosaLSL-YFP mice. Nuclei are visualized by DNA staining (DAPI, blue). *, p<0.05; n.s., not significant. (D and E) Quantification of single (yellow arrow) and adjacent (white arrows) YFP+ (red) hepatocytes in Transposon-CreER-injected RosaLSL-YFP (control) or cTKO;RosaLSL-YFP (TKO) mice at different time points after Tam. Cell membranes are visualized by immunostaining for β-catenin (green). Significances are shown between control and TKO cells 1 week after Tam. *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01. (F) Representative example of enlarged nuclei (DAPI, blue) in TKO hepatocytes (GFP+, green) in Transposon-CreER-injected cTKO;RosamTmG mice. Data in (B) and (E) are represented as mean +/− SD.