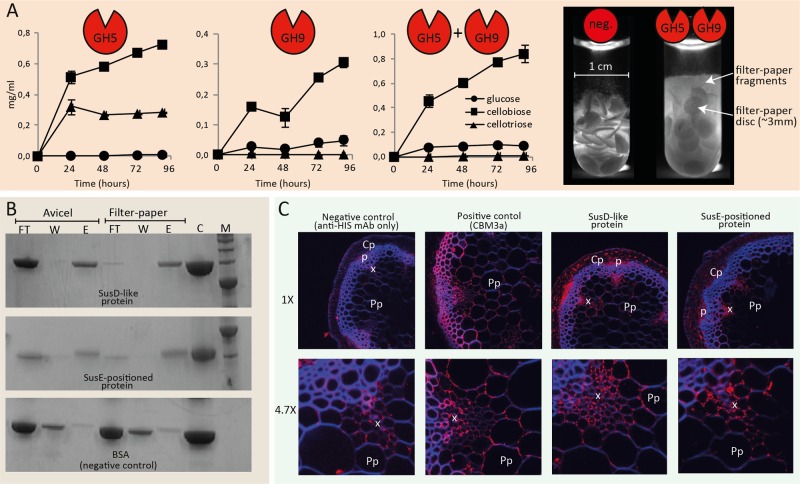
FIG 2 .
Biochemical characterization of cellulases and binding proteins encoded within the AC2a PUL. (A) Enzymatic activities of the GH5 and GH9 proteins determined by HPAEC-PAD analysis of products generated from filter paper (5%, wt/vol, 3 µM total enzyme concentration, pH 6.6). Error bars represent standard deviations between results of three replicates. The image to the right visualizes partial solubilization of filter paper discs after a 6-day incubation (discs were diluted 3:1 prior to image capture). neg., negative. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of fractions from pulldown assays using cellulosic substrates. Lanes: FT, unbound protein from supernatant fractions collected after a 1-h incubation and centrifugation; W, the wash fraction, containing protein washed off the substrate; E, eluted protein fractions where protein was released from the polysaccharides by boiling them in urea; C, control, where only the protein was loaded on the gel; M, a molecular weight standard. (C) Immunofluorescence labeling of A. thaliana cross sections using crystalline cellulose-binding CBM3a (positive control) as well as the SusD-like and SusE-positioned proteins from the AC2a cellulose-active PUL. Fluorescence from anti-His (in red) indicates bound protein, while autofluorescence, mainly in the interfascicular tissue, is blue. The SusD-like protein bound to cortical parenchyma (Cp)-, phloem (p)-, xylem (x)-, and pith parenchyma (Pp)-adjacent cell walls. The SusE-positioned protein showed weaker binding than the SusD-like protein and particularly targeted the intercellular junctions in the xylem tissue. The positive-control images were taken at lower gain due to high signals, while negative-control images were taken at higher gain. mAb, monoclonal antibody.