Figure 2.
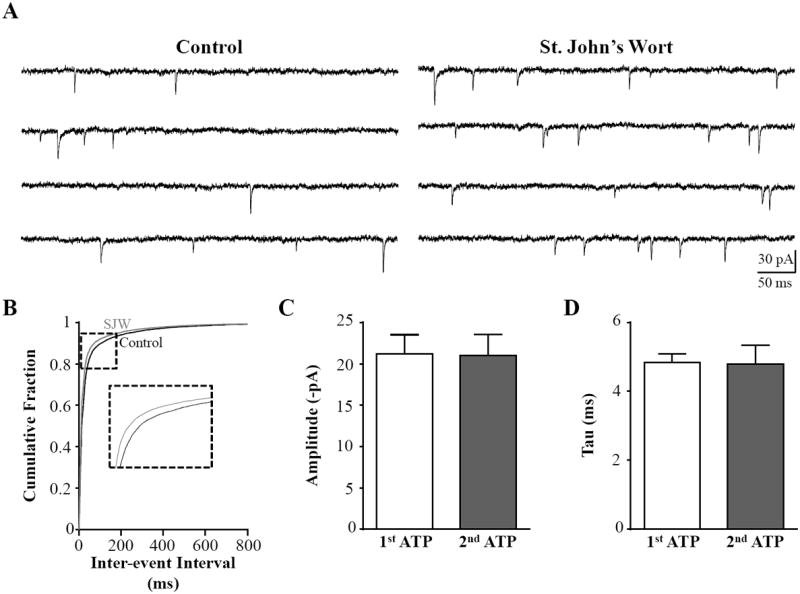
St. John’s Wort extract increases mEPSC frequency in NST neurons. A, We recorded mEPSCs (VHOLD=-60 mV) from NST neurons to evaluate whether St. John’s Wort extract caused increased quantal glutamate release from vagal afferent terminals. A representative control recording (left) was obtained in the presence of 10 μM bicuculline and 0.5 μM TTX. St. John’s Wort extract increased the frequency of events (right) in the same representative recording. B, The distribution of inter-event intervals was shifted significantly to the left in the presence of St. John’s Wort compared to control (Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, p < 0.05), suggesting that frequency of mEPSC events was increased by the extract. Neither peak amplitude (C) nor deactivation time course (D) was impacted by St. John’s Wort extract (paired t-test, p > 0.05). These data suggest that St. John’s Wort increases the probability of glutamate release from presynaptic vagal afferent terminals.
