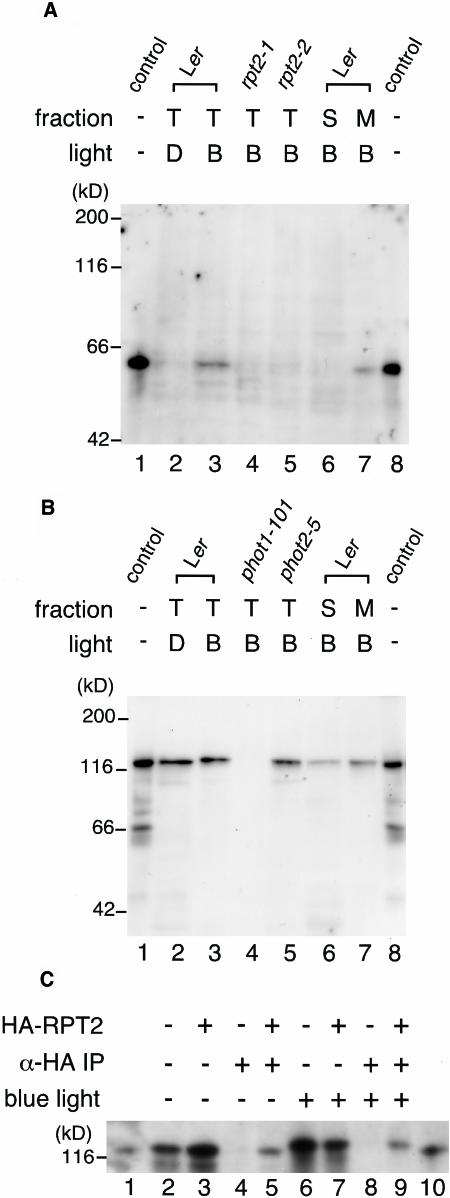
Figure 5.
Immunological Analysis of the Association of RPT2 with phot1.
(A) Immunoblot of RPT2. Etiolated wild-type seedlings (Ler; lanes 2, 3, 6, and 7), rpt2-1 seedlings (lane 4), and rpt2-2 seedlings (lane 5) were irradiated by blue light at 100 μmol·m−2·s−1 for 1 h (B; lanes 3 to 7) or were mock-irradiated (D; lane 2), and then fractions of total proteins (T; lanes 2 to 5), soluble proteins (S; lane 6), and crude microsomal proteins (M; lane 7) were prepared. Proteins (10 μg) in each fraction were separated by 8% SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-RPT2 antiserum. Lanes 1 and 8 show the molecular size marker of RPT2.
(B) Immunoblot of phot1. Etiolated wild-type seedlings (Ler; lanes 2, 3, 6, and 7), phot1-101 seedlings (lane 4), and phot2-5 seedlings (lane 5) were irradiated by blue light at 100 μmol·m−2·s−1 for 1 h (B; lanes 3 to 7) or mock-irradiated (D; lane 2), and then fractions of total proteins (T; lanes 2 to 5), soluble proteins (S; lane 6), and crude microsomal proteins (M; lane 7) were prepared. Proteins (10 μg) in each fraction were separated by 8% SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-phot1 antibody. Lanes 1 and 8 show the molecular size marker of phot1.
(C) Immunoprecipitation of the phot1–RPT2 complex. Etiolated wild-type seedlings (Ler; lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8) and transgenic seedlings expressing HA-RPT2 (lanes 3, 5, 7, and 9) were irradiated by blue light at 10 μmol·m−2·s−1 for 1 h (lanes 6 to 9) or mock-irradiated (lanes 2 to 5), and then fractions of crude microsomal proteins were prepared. These were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibody–conjugated agarose and then were separated by 6% SDS-PAGE, followed by immunoblotting with anti-phot1 antibody (lanes 4, 5, 8, and 9). Altogether 0.005 volumes of crude microsomal proteins used for immunoprecipitation were also electrophoresed without immunoprecipitation as a phot1 protein control (lanes 2, 3, 6, and 7). Lanes 1 and 10 show the molecular size marker of phot1.