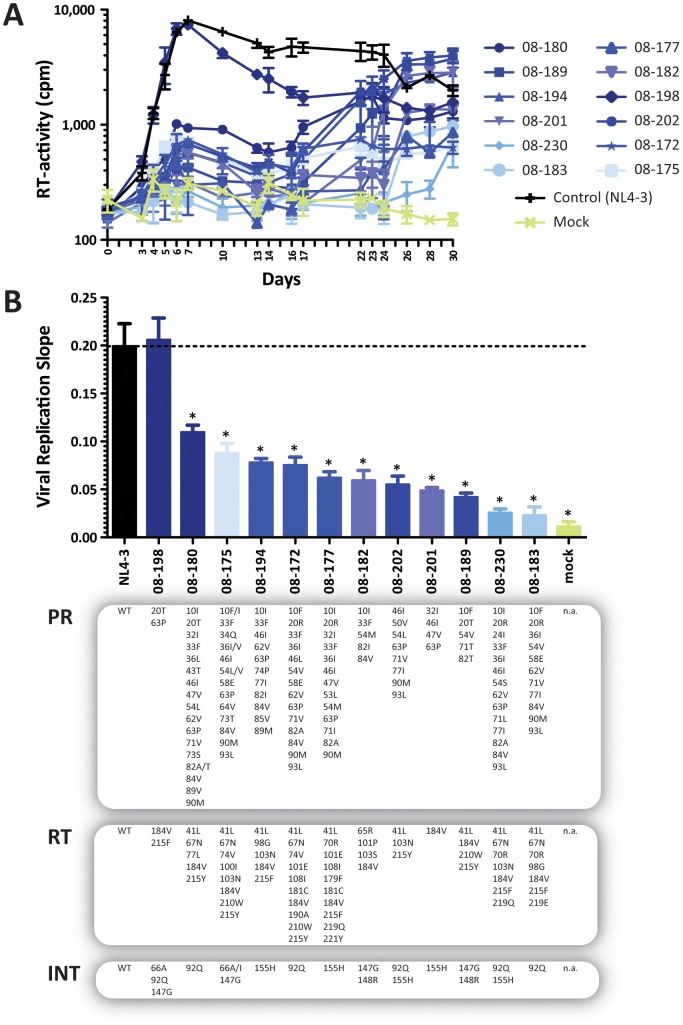
Figure 1. Replicative fitness of 12 patient-derived p2-INT-recombinant viruses in the absence of drug pressure.
(A) Thirteen p2-INT-recombinant viruses (i.e., 12 patient-derived and the HIV-1NL4-3 wild-type virus) were evaluated for their ability to replicate in MT-4 cells in the absence of drug pressure. Virus replication was quantified by measuring reverse transcriptase (RT) activity in the cell-free supernatant. (B) Viral replication slopes were calculated using the slopes between RLU values at days 0 & 3, 0 & 4, 0 & 5, 0 & 6, and 0 & 7, corresponding to exponential viral growth. All five slope values for each virus were used to calculate the mean, standard deviation, and 10th & 90th percentiles. Differences in the mean values were calculated using a One Way Analysis of Variance test and the significance difference from HIV-1NL4-3 calculated using the Bonferroni's Multiple Comparison Test. The replication kinetics of viruses marked with an asterisk (*) were significantly different to the HIV-1NL4-3 control (p<0.05, 95% CI). Mutations in the protease (PR), reverse transcriptase (RT), and integrase (INT) coding regions are indicated for each virus. WT, wild-type (HIV-1NL4-3 virus).