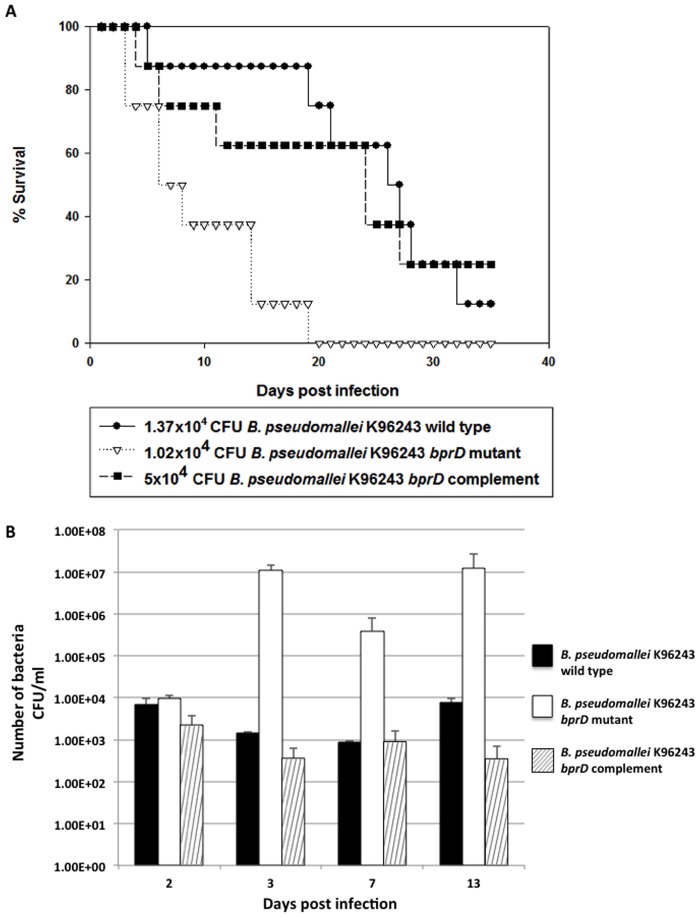
Figure 4. Survival curves and numbers of bacteria in the spleen of BALB/c mice after infection with B. pseudomallei.
(A) The virulence of the B. pseudomallei K96243 wild-type and bprD mutant strains was compared in BALB/c mice, which are highly susceptible to infection. X-axis, days after infection; Y-axis, % survival. BALB/c mice (groups of eight) were intraperitoneally infected with ∼104 CFU of the B. pseudomallei K96243 wild-type (•), bprD mutant (∇) or bprD complemented (▪) strain, and their survival was monitored daily. The survival of mice infected with the wild-type strain was significantly different from those infected with the bprD mutant (P = 0.0015). (B) The numbers of B. pseudomallei K96243 wild-type, bprD-mutant, and bprD-complemented strains in the spleen of BALB/c mice. X-axis, days after infection; Y-axis, number of bacteria (CFU). A total of 1×104 CFU of the wild-type (▪) and bprD-mutant (□) strains, and 0.5×104 CFU of the bprD-complemented (  ) strain, were intraperitoneally injected into BALB/c mice. The number of bacteria in the spleen on days 2, 3, 7 and 13 was determined. The experiment was performed twice; average values of data are shown.
) strain, were intraperitoneally injected into BALB/c mice. The number of bacteria in the spleen on days 2, 3, 7 and 13 was determined. The experiment was performed twice; average values of data are shown.