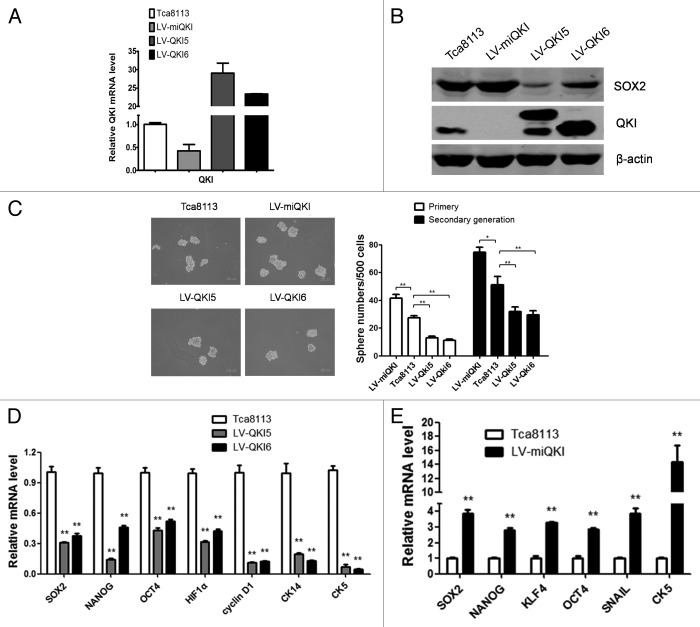
Figure 2. QKI inhibits stem cell properties of OSCC in vitro. (A) Expression of QKI in Tca8113 cells. Tca8113 cells infected with LV-miQKI, LV-QKI5, or LV-QKI6 were detected by qPCR. Data are shown as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. (B) Expression of QKI and SOX2 in Tca8113 cells. Tca8113 cells infected with LV-miQKI, LV-QKI5, or LV-QKI6 were detected by western blot. Overexpression of QKI reduced the protein level of SOX2, while knockdown of QKI increased the level of SOX2 in Tca8113 cells. (C) LV-miQKI cells formed more primary and secondary passaged spheres than the control cells, while LV-QKI5 or LV-QKI6 cells formed fewer primary and secondary passaged spheres than the control cells. Shown are representative phase-contrast image of spheres derived from cells (scale bar = 200 μm). Data are shown as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. (D) qPCR analysis was performed for the indicated genes in Tca8113, LV-QKI5, or LV-QKI6 cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01. CK5, cytokeratin 5; CK14, cytokeratin 14. (E) qPCR analysis was performed for the indicated genes in Tca8113 or LV-miQKI cells. Data are shown as mean ± SD from 3 independent experiments. **P < 0.01.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.