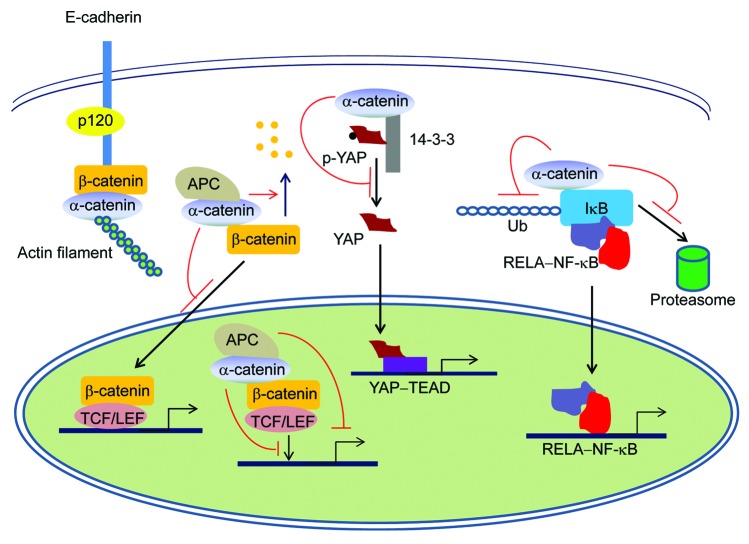
Figure 1. α-catenin signaling in cancer. In addition to maintaining the integrity of the cadherin-catenin complex and linking adherens junctions to the actin cytoskeleton, α-catenin can: (1) inhibit the Wnt/β-catenin pathway by preventing β-catenin nuclear translocation or formation of the β-catenin-TCF-DNA complex, by promoting β-catenin degradation, or by recruiting APC to the β-catenin-TCF complex; (2) regulate the Hippo-YAP pathway by blocking YAP dephosphorylation and nuclear localization; and (3) suppress the NF-κB pathway by inhibiting IκB ubiquitination and its association with the proteasome, in a tissue type-specific manner. The Hedgehog pathway is not shown, as it is unknown how this pathway is regulated by α-catenin.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.