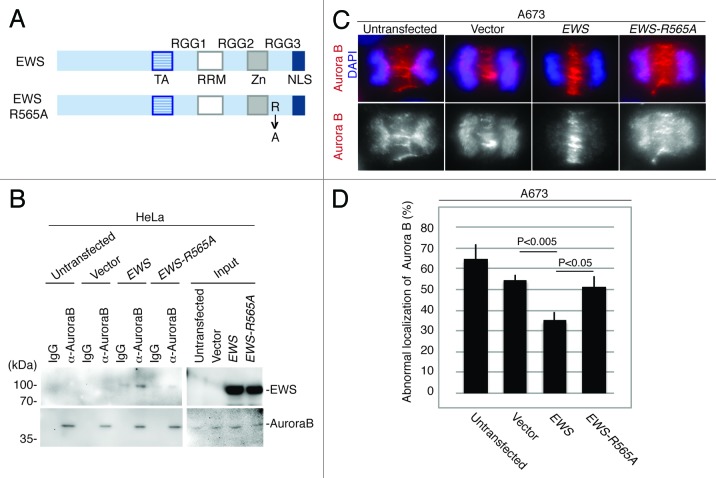
Figure 4.
EWS but not EWS-R565A mutant interacts with Aurora B, and transfection with EWS but not EWS-R565A mutants rescues the high incidence of the aberrant localization of Aurora B in A673 cells. (A) Schematic drawing of EWS and EWS-R565A mutant proteins. (B) Immunoprecipitation of lysates from untransfected, empty vector, pSG5-2xFLAG-EWS- and pSG5-2xFLAG-EWS-R565A mutant-transfected HeLa cells using IgG and anti-Aurora B antibody. Top (left), probing blots with anti-FLAG shows that EWS coimmunoprecipitates with Aurora B. Bottom; left, Probing blots with anti-Aurora B shows immunoprecipitation of endogenous Aurora B; right, input sample (1/50) of cell lysates of untransfected, empty vector, pSG5-2xFLAG-EWS- and pSG5-2xFLAG-EWS-R565A-transfected HeLa cells demonstrated with anti-FLAG antibody (top) and anti-Aurora B antibody (bottom). (C) Top, merged images with DNA stained with DAPI (blue), and Aurora B (red) visualized with anti-Aurora B antibody; bottom, Aurora B visualized with anti-Aurora B antibody in A673 cells. (D) Percentages of cells with abnormal localization patterns for Aurora B were scored in untransfected, empty vector, pSG5-2xFLAG-EWS- and pSG5-2xFLAG-EWS-R565A-transfected A673 cells (50 anaphase were scored for each of the experiment) (n = 3 experiments).